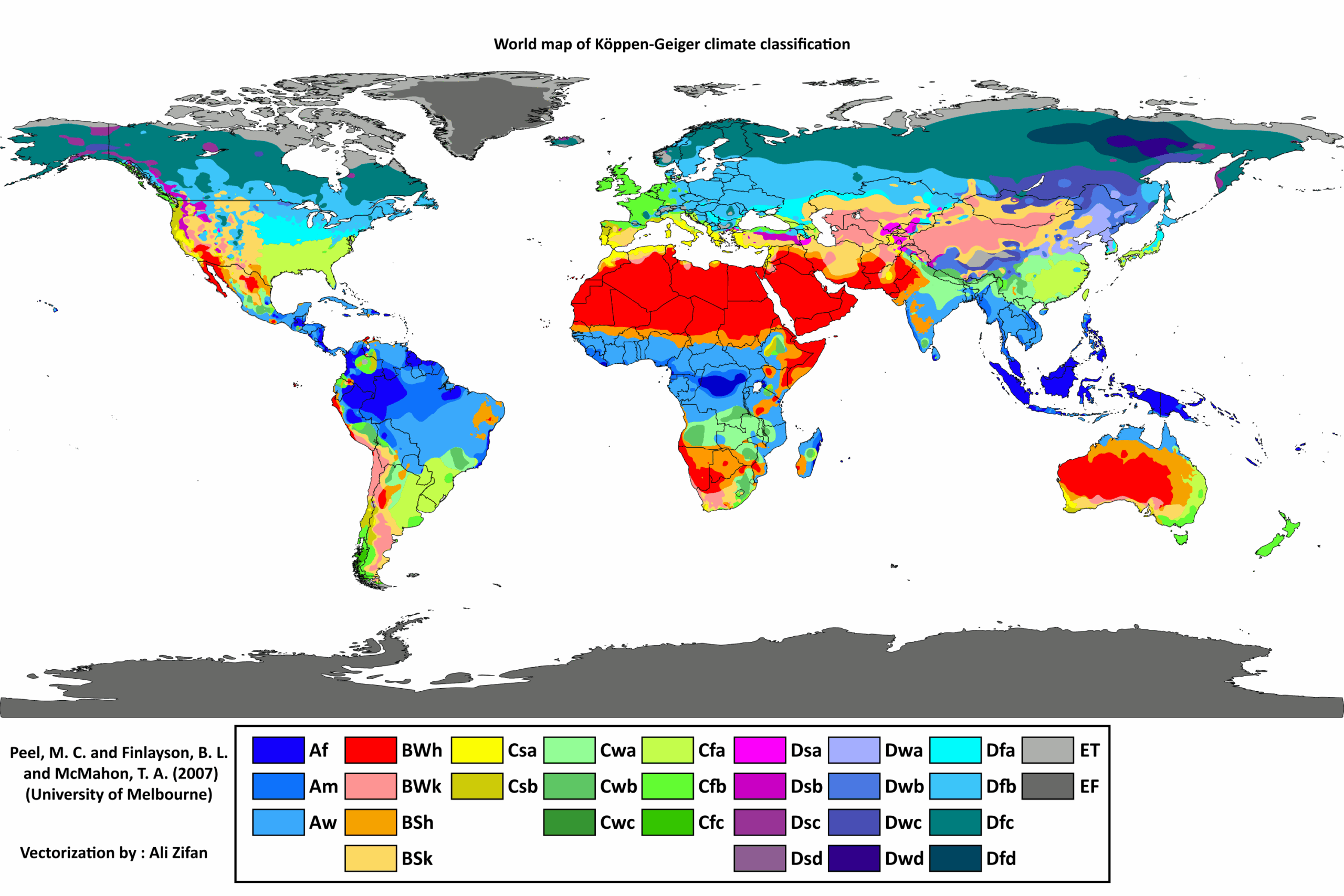
In recent years, the contentious debate surrounding climate change has intensified, capturing the attention of scientists, policy-makers, and the general public alike. This discourse has witnessed an upsurge of climate skeptics—individuals who question the prevailing scientific consensus regarding anthropogenic climate change. A recent survey dispelling these skeptical attitudes presents a scientific rebuttal that deserves attention for its implications and the underlying reasons for the fascination with climate skepticism.
The skepticism surrounding climate change often stems from a fundamental misunderstanding of scientific methodologies and the nature of scientific inquiry. Many skeptics point to uncertainties in climate models or emphasize natural climatic variability as evidence against the dominant narrative of human-induced change. However, the recent survey illuminates the overwhelming scientific consensus that underscores the reality of climate change. A staggering percentage of climate scientists affirm that human activities are significantly impacting the planet’s climate systems.
One must delve deeper into the psychological and sociocultural dimensions that underpin climate skepticism. Cognitive dissonance plays a pivotal role; individuals confronted with evidence conflicting with their preconceived notions may experience discomfort, leading them to reject new information. This cognitive bias often finds its roots in ideological beliefs, particularly in socio-political contexts where acceptance of climate change may implicitly challenge one’s worldview. Therefore, the resistance to acknowledging climate change mirrors broader societal conflicts surrounding ideological and political affiliations.
Moreover, the marvel of climate skepticism also captivates attention due to the allure of contrarian thinking. There exists an intrinsic fascination with dissent, particularly in a scientific context where consensus is often equated with rigor and reliability. The skepticism invites a kind of intellectual curiosity, provoking individuals to question established norms and seek alternative explanations. However, this allure can be dangerous, as it may lead to the dissemination of misinformation and undermine public understanding of critical scientific issues.
The survey highlights another crucial aspect: the role of media in shaping perceptions of climate science. The portrayal of skepticism within various media outlets often creates a false equivalence between scientific consensus and dissenting voices, fostering a misleading impression of uncertainty surrounding climate change. This phenomenon, commonly referred to as “false balance,” can skew public perception, leading to confusion and skepticism where scientific agreement prevails. It is vital for media entities to navigate this delicate terrain, ensuring that their representations accurately reflect established scientific understanding.
Furthermore, the economic implications intertwined with climate change discourse cannot be overstated. Fossil fuel industries, in particular, have vested interests in perpetuating skepticism, as it serves to protect their financial interests amidst burgeoning environmental regulations. By funding research that casts doubt on climate change or promoting skeptics through various channels, these industries contribute to a culture of confusion that stifles meaningful discourse. The financial clout behind climate skepticism underscores an intricate web of economic motivations at play, complicating the push for an environmentally responsible paradigm.
Another factor to consider is the geographical and socioeconomic disparities in perceptions of climate change. Communities that are more vulnerable to economic instability may prioritize immediate concerns over long-term climatic projections, leading to a dismissal of climate science that does not resonate with their immediate experiences. Addressing these disparities requires a nuanced understanding that bridges the gap between scientific communication and the local experiential realities of diverse populations. Sustainable solutions to climate change must be integrated into the socioeconomic fabric of affected communities to foster greater acceptance.
On a more optimistic note, the survey also emphasizes the growing momentum for climate action. An increasing number of individuals, especially the youth, are becoming more environmentally conscious, advocating for policies that mitigate climate change. This shift indicates a generational transformation where skepticism is being challenged by environmental stewardship and responsibility. The commitment to climate activism among young people reflects a repudiation of previously held skeptical views, further solidifying the need for educational initiatives that emphasize scientific literacy and environmental awareness.
Furthermore, an essential strategy in combating skepticism lies in enhancing public engagement with climate science. Outreach efforts that demystify scientific processes and emphasize community involvement can foster a sense of ownership over environmental issues. Programs that promote hands-on experiences—such as community-supported agriculture or local climate action initiatives—can engender a profound connection to the environment, thus reducing skepticism and encouraging proactive behaviors.
In conclusion, while climate skepticism persists within public discourse, emerging surveys provide critical insights that highlight the prevailing scientific consensus. Understanding the psychological, sociocultural, and economic underpinnings of skepticism is crucial to addressing its impact on public perception. By fostering informed dialogue, enhancing scientific literacy, and advocating for proactive engagement, society can navigate the complexities of climate change skepticism. Ultimately, uniting in a collective commitment to environmental stewardship is essential for building a sustainable future that prioritizes the well-being of the planet and all its inhabitants.