The European Organization for Nuclear Research, known as CERN, stands as a bastion of scientific inquiry and technological advancement, dedicated to unraveling the fundamental mysteries of the universe. Established in 1954, CERN has been at the forefront of high-energy physics, consistently pushing the boundaries of our understanding of matter and the forces that govern it. This extensive examination of CERN’s achievements will elucidate the organization’s contributions across multiple domains, including fundamental discoveries, technological innovations, and its impact on society and education.
1. Fundamental Discoveries in Particle Physics
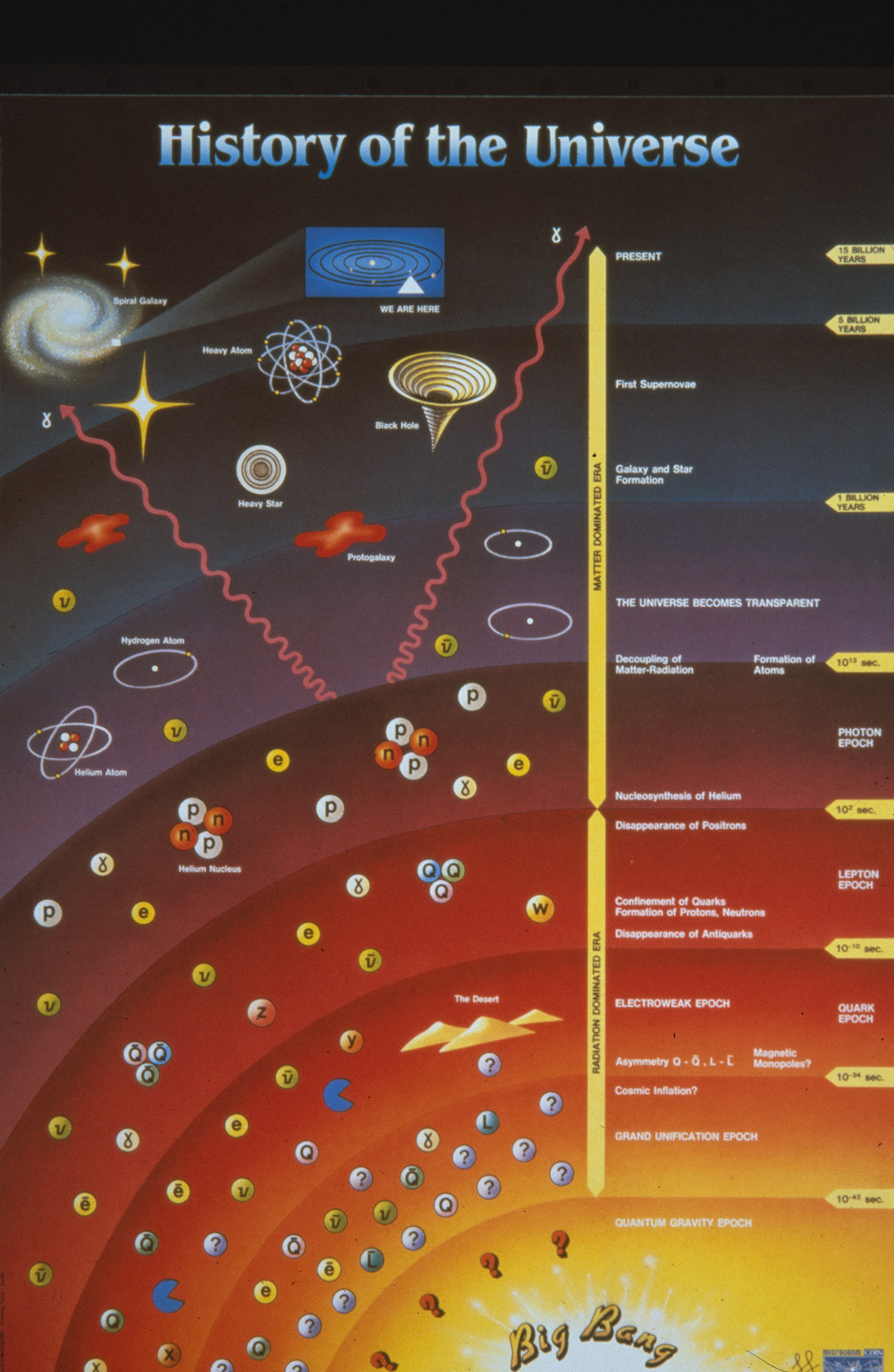
At the core of CERN’s mission lies the pursuit of fundamental knowledge in particle physics. The laboratory is home to the Large Hadron Collider (LHC), the world’s most powerful particle accelerator. One of the LHC’s most notable achievements was the discovery of the Higgs boson in July 2012. This elusive particle, often described as the “God particle,” provides a mechanism that explains how particles acquire mass through the Higgs field. The discovery confirmed the existence of a pivotal element of the Standard Model of particle physics, a theoretical framework that describes the electromagnetic, weak, and strong nuclear interactions.
Moreover, CERN’s research has contributed significantly to the study of antimatter. The ALPHA experiment has successfully captured antihydrogen atoms, allowing physicists to investigate the properties of antimatter and explore questions regarding the asymmetry between matter and antimatter in the universe. Such inquiries may hold the key to understanding why our universe is predominantly composed of matter, despite the expectation that matter and antimatter should have been produced in equal quantities during the Big Bang.
2. Advancements in Technology
Beyond its scientific discoveries, CERN has been instrumental in pioneering technologies that extend beyond the realm of particle physics. The organization has played a crucial role in the development of the World Wide Web. In 1989, Tim Berners-Lee developed the first web browser while working at CERN, facilitating the dissemination of information among researchers and ultimately transforming the Internet into a ubiquitous platform for communication and knowledge sharing.
Additionally, CERN has spearheaded advancements in detection technologies and instrumentation that are critical not only for future experiments but also for various applications in medicine and industry. The innovations in imaging technologies, particularly in the field of medical diagnostics such as cancer treatment methodologies using proton therapy, underscore CERN’s broader impact on society. The technologies originally developed for particle physics experiments have been adapted to improve the precision and efficacy of medical treatments.
3. Global Collaboration
CERN exemplifies international cooperation in scientific research, bringing together thousands of scientists, engineers, and researchers from over 100 countries. The collaborative nature of CERN allows for diverse perspectives and expertise to converge, fostering a rich environment for scientific innovation. This multinational collaboration extends beyond the laboratory; it cultivates a global network of educational programs and outreach initiatives aimed at inspiring the next generation of scientists.
Programs such as the CERN Summer Student Programme and the Open Days events encourage young people to engage with science and technology. With millions of visitors attending these events, CERN has effectively become a platform for science communication, demystifying complex concepts and promoting science literacy within the public domain.
4. Addressing Societal Challenges
CERN’s contributions extend into the realm of societal applications, addressing some of the pressing challenges faced by humanity today. The organization’s research into fundamental particles and forces not only enriches our theoretical understanding of the universe but also provides insights into complex phenomena relevant to cosmology and astrophysics. The advancements made in particle physics have implications for understanding dark matter and dark energy, two of the most significant and perplexing constituents of the universe, which influence the cosmos’s structure and evolution.
Furthermore, CERN’s commitment to sustainability and resource efficiency is vital as the global community grapples with climate change and environmental degradation. Initiatives such as the CERN Green initiative aim to reduce the organization’s carbon footprint and promote sustainable practices in research and operations.
5. Future Prospects and Endeavors
Looking ahead, CERN’s plans include the Next Circular Collider (FCC), which aims to extend the understanding of the Higgs boson and explore new physics beyond the Standard Model. The anticipated capabilities of this proposed collider could allow scientists to probe deeper into questions regarding dark matter, supersymmetry, and the gravitational forces that shape our universe.
Additionally, CERN’s focus on understanding the early universe, particularly during the first few moments after the Big Bang, continues to drive research efforts. The knowledge garnered from these endeavors may reveal insights into the fundamental nature of reality itself, altering our comprehension of the universe’s origins and its ultimate fate.
Conclusion
CERN has undeniably achieved monumental feats in the fields of particle physics, technological advancement, and societal impact. The discoveries made at CERN have helped to shape our understanding of the universe while fostering a spirit of collaboration and innovation. The organization stands as a testament to the power of scientific inquiry and the profound implications of understanding the fundamental building blocks of nature. As CERN continues to push the boundaries of human knowledge, its legacy will undoubtedly influence future generations of scientists and technologists engaged in the quest to unravel the mysteries of the cosmos.