Energy and environmental management represent a multifaceted field that integrates the conscientious utilization of energy resources while ensuring ecological preservation. This discipline encapsulates a spectrum of activities ranging from the optimization of resource consumption to strategic planning in favor of sustainable development. Within an increasingly energy-dependent society, the importance of this sphere cannot be overstated; it delves into both the technical and philosophical realms of environmental stewardship and energy efficiency.
The concept of energy management is steeped in the manipulation and regulation of energy flows to meet economic, environmental, and societal goals. Essentially, it involves the systematic planning and application of measures aimed at improving energy efficiency, thereby reducing costs and minimizing negative environmental impacts. The primary objective is to ensure that energy consumption occurs at optimal levels—satisfying both current demand and future sustainability without compromising the health of our planet.
In conjunction with energy management, environmental management emphasizes the strategic oversight of natural resources to safeguard ecosystems while accommodating human activities. This involves not merely a reactive approach to environmental degradation, but also a proactive stance that anticipates potential ecological disturbances. Central to this discourse is the recognition that human interactions with the environment can have unforeseen consequences, compelling a shift in how organizations and governments approach resource utilization.
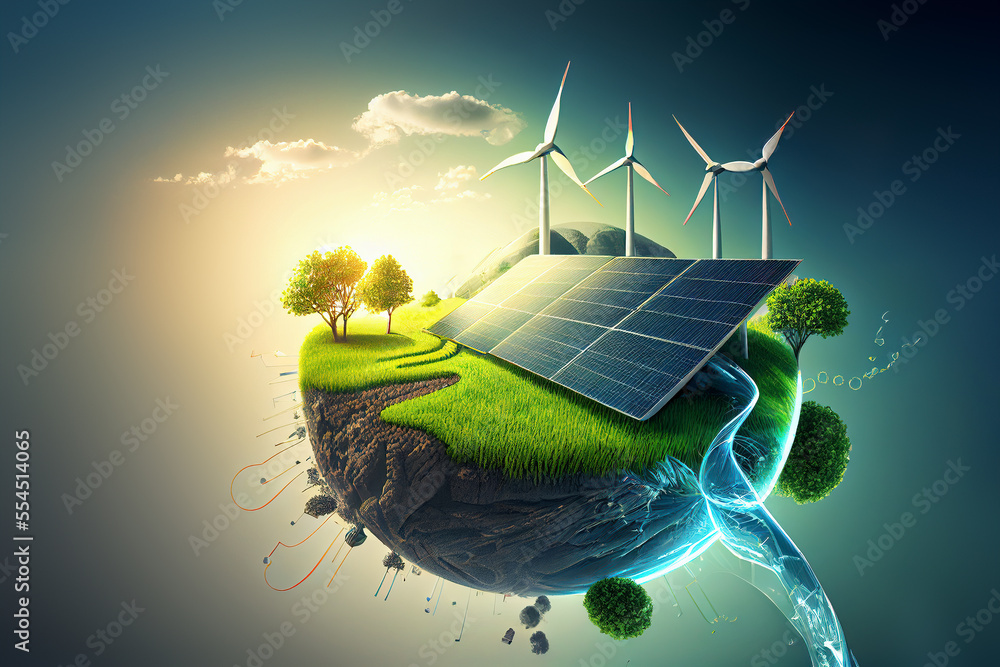
The interrelationship between energy and environmental management becomes more apparent when examining contemporary energy sourcing. Conventional energy sources, such as fossil fuels, have been historically favored for their abundance and cost-effectiveness. However, their extraction and utilization are fraught with ecological ramifications, including air pollution, climate change, and biodiversity loss. Consequently, there is a growing predilection towards renewable energy sources—wind, solar, and geothermal—that promise a more harmonious coexistence with the natural world.
Wind and solar energy, emblematic of the renewable sector, present an intriguing dichotomy with respect to energy management. Wind turbines, for instance, harness kinetic energy from the atmosphere, converting it into electrical power while exerting minimal environmental strain. The deployment of such technologies not only cultivates a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions but also offers a dialogue concerning energy policy, economic incentives, and technological advancements. Similarly, the solar industry burgeons, transforming sunlight into usable energy and engendering discussions about domestic versus commercial energy sources.
However, the transition to renewable sources is not without its challenges. Issues surrounding intermittency—the irregular generation of energy depending on weather and time—raise questions as to how energy systems can be effectively designed to maintain reliability. Storage technologies, such as batteries and pumped hydro storage, play a pivotal role in mitigating these issues. Moreover, the integration of smart grid systems facilitates a more responsive and flexible approach to energy distribution and consumption.
Environmental management encompasses several strategic frameworks to address ecosystem protection and resource conservation. Principles such as the precautionary approach advocate for foresight when addressing potential environmental risks, promoting a philosophy that urges caution in the face of uncertainty. These principles are especially salient in the context of energy projects where ecological repercussions can be substantial and last for generations.
In recent years, the concept of sustainability has gained traction within both energy and environmental management. The pursuit of sustainability seeks to balance economic growth, social equity, and environmental protection, leading to a holistic model of resource use. Corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives in the energy sector strive to uphold sustainable practices by implementing transparent reporting mechanisms, embracing circular economy principles, and fostering stakeholder engagement. Organizations are increasingly recognizing that fostering a positive environmental image may enhance their competitiveness and appeal to a conscientious consumer base.
The philosophical underpinnings of environmental and energy management cannot be overlooked. They compel us to contemplate the ethical dimensions of our choices. Homo sapiens, as custodians of the Earth, bear a profound responsibility to mitigate their impact on the biosphere. This elucidates the intricate balance required in decision-making processes that encompass ecological integrity and societal welfare. The intricate connection between human activities and environmental health propels an ongoing narrative, steering humanity toward more considerate consumption patterns.
Ultimately, energy and environmental management embody a convergence of science, ethics, and economic considerations. This interdisciplinary nexus presents numerous avenues for exploration and innovation: from technological advancements in energy efficiency and renewables to policy frameworks that advocate for environmental conservation. As the specter of climate change looms ever larger, embracing such holistic and integrated management practices becomes an imperative rather than an option. The allure of this domain lies not only in its technical complexity but also in its profound implications for future generations.
In conclusion, energy and environmental management serve as pivotal disciplines that traverse the landscape of modern civilization. They invite critical examination of our entwinement with the natural world while urging multifarious stakeholders to actively participate in shaping a sustainable future. The confluence of energy efficiency with ecological prudence is a notable testament to human ingenuity and a clarion call for responsible stewardship of our irreplaceable planetary resources.