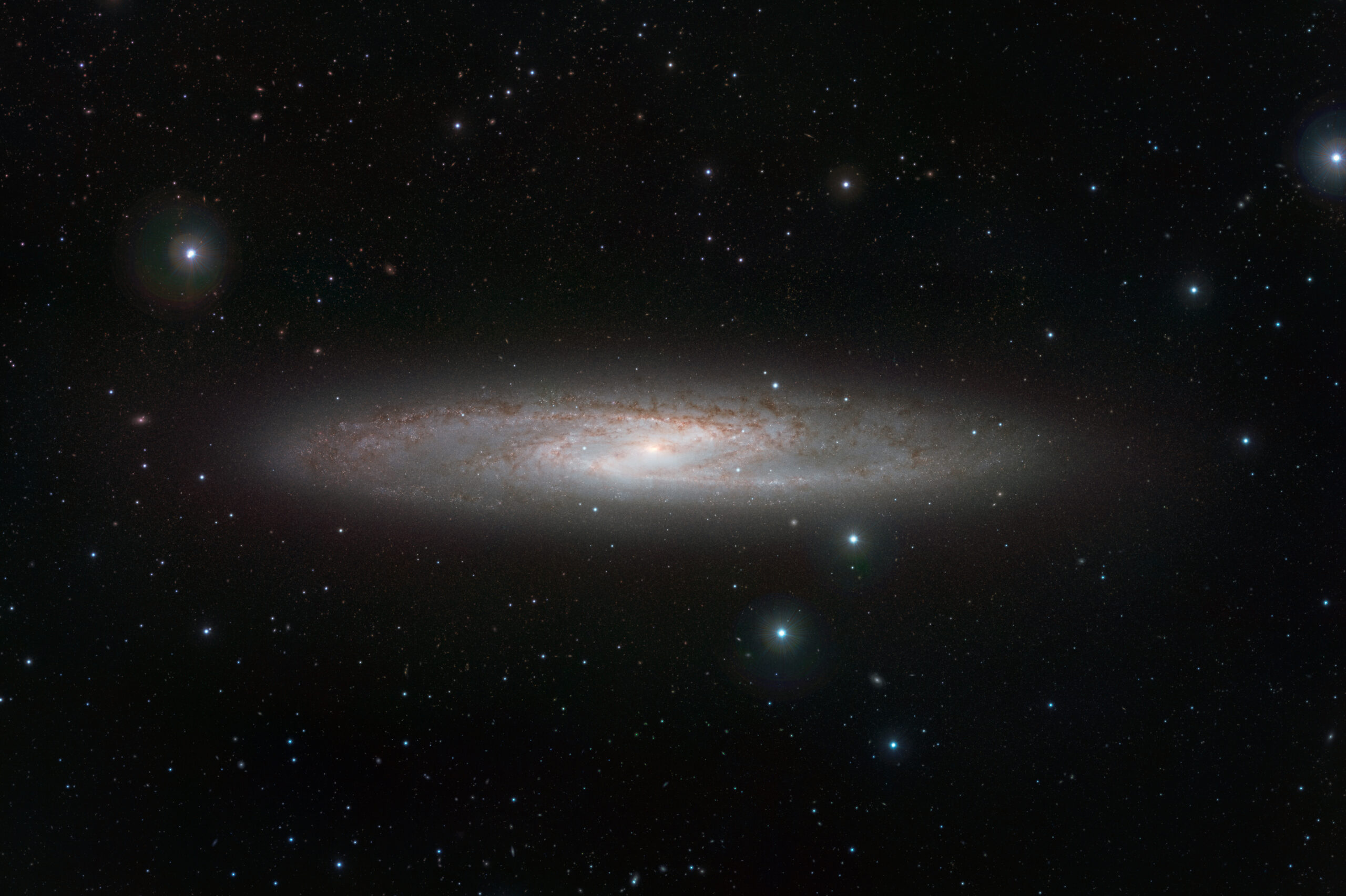
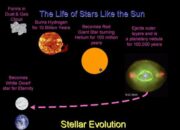
The cosmos has always captivated human imagination, serving as a crucible for scientific inquiry and philosophical contemplation. The Milky Way, alongside its neighboring celestial formations, continues to unveil unprecedented galactic phenomena that beckon exploration. In recent epochs, multiple records within the grand tapestry of the universe have emerged, invigorating both the scientific community and the public’s fascination with the cosmic expanse.
One significant area of focus is the prolific discovery of exoplanets residing within the habitable zones of their respective stars. These newfound worlds—often dubbed “Goldilocks planets”—exhibit conditions that could potentially harbor life. The sheer number of identified exoplanets has catalyzed a paradigm shift in our understanding of planetary formation and residence. Data gathered from missions such as Kepler and TESS (Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite) have yielded thousands of candidate exoplanets, each presenting unique characteristics that defy previously established notions of planetary systems. The prospect of life beyond Earth is not merely a tantalizing notion but rather supported by statistical plausibility given the vast number of stars and their planets.
Beyond the immediate fascination with these planets is the underlying implication of an abundance of conditions conducive to life. The discovery of a planet that possesses liquid water, atmospheric diversity, or even geological activity prompts deeper inquiries into the nature of life itself. Researchers are compelled to contemplate the universality of life’s biochemical frameworks, leading to astrobiological implications that extend our understanding of life’s potential variations across the cosmos.
Furthermore, the enigma of black holes remains a record-breaking phenomenon worthy of scrutiny. With the recent imaging of the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way, known as Sagittarius A*, from gravitational wave detections to the Event Horizon Telescope’s visualizations, the astrophysical community stands at a precipice of enhanced comprehension of these enigmatic entities. The implications are enormous, challenging notions of gravity, spacetime, and the fundamental structure of our universe.
Black holes not only elucidate the nature of gravity but also serve as critical components in our cosmological narrative. Their interactions with surrounding matter provide insights into the formation and evolution of galaxies. The staggering masses of these black holes, often millionfold that of our Sun, illuminate the correlation between galaxy growth and black hole accretion. The transfer of matter towards these celestial behemoths produces energetic jets that can affect star formation across significant galactic neighborhoods. This interplay underscores a symbiotic relationship between supermassive black holes and galaxy dynamics, further captivating the scientific community.
In the quest to elucidate galactic phenomena, the advent of advanced telescopic technology has magnified observational capabilities, yielding records in distance and detail. Instruments such as the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) have begun to deliver unprecedented images of deep-space entities, enabling astronomers to observe the universe’s earliest epochs. These observations not only substantiate existing theoretical frameworks but also raise new questions regarding the formation of stars and galaxies. The clarity with which JWST captures distant galaxies allows for more refined models of cosmic evolution, shedding light on the timeline of our universe.
Moreover, the detailed study of these protoplanetary disks around young stars reveals an intricate dance of dust and gas, ultimately leading to planet formation. High-resolution spectrographs facilitate the identification of molecular signatures within these disks, illuminating the chemical precursors to life. This interconnectedness between cosmic phenomena underscores a delicate balance of forces at play within the universe. As such, each new discovery enlightens our position within the broader cosmic landscape.
In conjunction with the galactic advancements mentioned, the emergence of dark matter as a dominating force within cosmic structure has become a focal point for researchers. Dark matter, while elusive, constitutes approximately 27% of the universe’s mass-energy content, significantly shaping the gravitational framework of galaxies. Each new experiment aiming to probe the qualities of dark matter further underscores the riddle of its nature and its pervasive influence throughout the universe.
Research employing gravitational lensing, where massive objects warp light from distant galaxies, has provided a revolutionary perspective on the distribution of dark matter. These observations have led to the formulation of new theories and paradigms about the structure of the universe. As each new record regarding the behavior and properties of dark matter is unveiled, the dialogue surrounding the fundamental constituents of our cosmos effectively deepens.
In summary, the allure of the galaxy’s new records transcends mere statistical information. It encapsulates a deeper method of pondering our existence and the myriad of mysteries that lie interspersed within the void. The bewitchment lies not only in numbers but in the stories they tell. Each discovered record in galactic dynamics or the narrative of black holes reframes our comprehension of the universe and beckons us to reflect on our place within it. As humanity navigates this ever-expanding cosmic frontier, we remain drawn to the unknown, propelled by an insatiable curiosity that is at the very heart of the scientific endeavor.