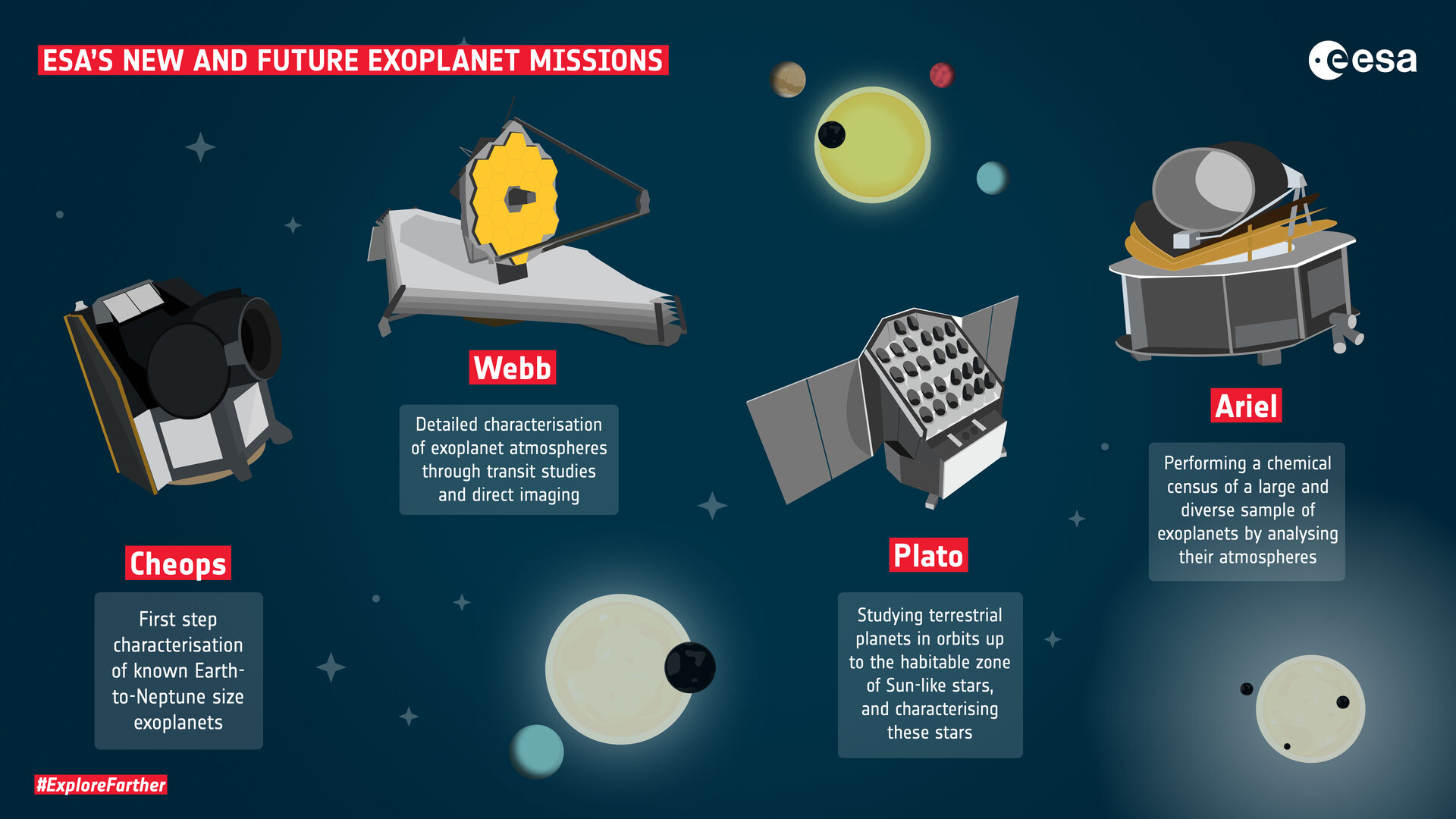
The exploration of Mars tantalizes humanity with its profound enigmas—vast plains of rust-colored regolith, towering volcanoes, and the intriguing possibility of ancient microbial life. The European Space Agency (ESA) is charting a Martian future that promises to deepen our comprehension of the Red Planet, paving the way for transformative scientific discoveries. As the exploits of the past collide with the aspirations of the future, a compelling narrative unfolds regarding the emergence of Martian missions that resonate with the spirit of exploration.
ESA’s enthusiasm for Martian endeavors warrants a closer examination, particularly as these missions symbolize humanity’s innate desire to transcend earthly boundaries. The prospect of unraveling Martian mysteries stirs the imagination, compelling scientists and laypeople alike to envision a vibrant tapestry of the Red Planet’s past, present, and future. With a focus on astrobiology, geology, and planetary science, ESA’s mission portfolio composes a symphony of interplanetary initiatives that has far-reaching implications for our civilization.
At the crux of this Martian narrative lies the ExoMars program, a collaborative effort between ESA and the Russian space agency Roscosmos. This ambitious initiative manifests in various phases, with the rover and surface science platform slated for launch in the near future. In the heart of this program resides the Rosalind Franklin rover—a tribute to the luminary whose work in molecular biology unlocked the secrets of life on Earth. As this rover embarks on its odyssey across Martian terrain, it serves as a vehicle of curiosity targeted at deciphering organic compounds, thereby investigating whether life once flourished on the Red Planet.
In an enchanting dance with ambition, the ExoMars rover epitomizes a fusion of engineering ingenuity and scientific zeal. With its suite of sophisticated instruments, including a drill capable of penetrating the Martian crust to unearth subsurface samples, the rover becomes a digital archaeologist, excavating layers of the planet’s history to construct a narrative of its climatic evolution. As it scours the landscape, it seeks to establish a geological chronicle that bridges the gap between its dusty surface and the potential oasis life once inhabited.
The ambitious trajectory of ESA is not limited to ExoMars. The agency is also engaged in an array of missions designed to investigate the planet’s atmosphere and surface conditions. The Mars Express orbiter, a longstanding sentinel in orbit, has significantly contributed to understanding Martian features, including its polar ice caps and ancient riverbeds. Through its continued operations, this mission highlights a transformative reality—Mars is not merely a distant world, but a dynamic entity with a history that beckons for interpretation.
Complementing ExoMars, the upcoming Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (JUICE) mission signifies ESA’s multifaceted approach to planetary exploration. While the primary targets of JUICE are the icy moons of Jupiter, its overarching ethos pertains to the study of planetary bodies, engendering a platform for comparative planetology. As scientists glean insights from diverse environments, including Jupiter’s icy satellites and Mars’s arid landscapes, they witness the universality of geological processes and the potential for life across disparate celestial realms.
The emergence of these missions embodies not merely an aspiration to explore but to foster an international consortium dedicated to unlocking the secrets of the cosmos. ESA’s collaborative partnerships extend beyond Europe, resonating within the framework of the Artemis program led by NASA. Such partnerships cement a pioneering spirit that extends to collaborative Martian exploration efforts in the coming decades. Joint missions could entail shared technological innovations and a pool of resources, fortifying the foundations upon which humanity can build its Martian future.
As these missions gain momentum, the multidimensional benefits of Mars exploration become abundantly clear. Applications extend into terrestrial sciences, and technologies developed for Martian exploration—such as advancements in robotics, AI, and telecommunication—can be harnessed to ameliorate conditions on Earth. Moreover, cultivating a deeper understanding of planetary habitability underpins endeavors in addressing pressing existential challenges faced by humanity today, including climate change and resource scarcity.
The allure of Martian exploration extends beyond the rational realms of scientific inquiry; it has woven itself into the fabric of popular culture and humanity’s collective psyche. The Red Planet invokes a sense of wonder and intrigue, inspiring artistic expressions in literature, film, and art. This cultural resonance serves as a catalyst for championing STEM education, engendering curiosity in younger generations who may one day become the explorers of tomorrow. Thus, the missions undertaken by ESA transcend the mere achievement of scientific milestones; they captivate the imagination and inspire a vision of humanity’s place within a broader cosmic narrative.
With each passing year, as ESA charts its Martian trajectory, it propels humanity into a future brimming with potential. The tantalizing prospect of learning from the Martian landscape ignites a spark of collective ambition, urging nations to unite in collaborative endeavors that venture beyond conventional borders. The exploration of Mars calls forth an intricate interplay of science, culture, and philosophy, unfurling an odyssey that holds profound implications for our understanding of life itself. The future beckons, and as the tapestry of interstellar exploration unfolds, it invites all of humanity to partake in this extraordinary quest toward understanding the enigmatic allure of the Red Planet.