The cosmos is replete with awe-inspiring phenomena that evoke an innate sense of wonder within humanity. Among these, cosmic dust remains one of the most intriguing subjects for both astrophysicists and laymen alike. The term “dust watcher” encapsulates the curiosity surrounding these minuscule entities that, while often overshadowed by grand celestial bodies, play a crucial role in the formation of galaxies, star systems, and even life itself. This exploration will delve into the CODAG (Cosmic Dust Aggregation) Chronicles by examining the multifaceted significance of cosmic clumps, hinting at the deeper reasons underlying humanity’s fascination with these ephemeral particles.
To understand cosmic dust, one must first define its fundamental characteristics. Cosmic dust is a mixture of microscopic particles predominantly composed of silicates, carbonaceous materials, and ices, originating from various cosmic processes, including stellar death, supernova explosions, and the accretion processes within protoplanetary disks. These particles are not merely trivial minutiae; they serve as fundamental building blocks in the vast interstellar medium. Within this context, influences of gravity initiate processes that lead to the aggregation of these dust grains, forming clusters and eventually lending themselves to the genesis of more substantial cosmic structures.
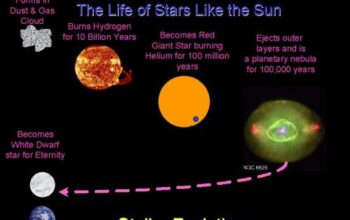
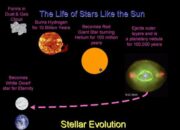
The concept of CODAG embodies the intricate narratives told through dust clumps’ formation and evolution over eons. Every aggregation of dust tells a story, a record of the cosmos’ history and its transformative processes. For instance, when large collections of cosmic dust coalesce within dense molecular clouds, they can instigate the gravitational collapse necessary to form stars. This stellar genesis is pivotal, as it is from stars that the heavier elements required for the formation of planets—and eventually, life—are synthesized through nuclear fusion. Hence, cosmic clumps can be viewed as both the progenitors of stellar systems and as repositories of the universe’s elemental heritage.
This profound relationship between cosmic dust and the formation of stars and galaxies raises an essential question: what drives humanity’s fascination with such insubstantial particles? One may argue that this fascination stems from our cosmic origins, as we are, in essence, stardust ourselves. The notion that the very atoms comprising our anatomy were birthed in the hearts of ancient stars resonates deeply within us. Dust, therefore, is emblematic of a profound connection that transcends temporal and spatial boundaries, acting as a bridge between the microcosm of our existence and the macrocosm of the universe.
In addition to their role in the cosmic narrative, dust particles are also pivotal for understanding the evolutionary dynamics of galaxies. Through the study of dust clouds in various galactic environments, astrophysicists gain insight into the processes governing star and planet formation, galactic cooling mechanisms, and even the dynamics of dark matter. Observations from both ground-based and space telescopes have revealed that dust distribution varies significantly across galaxies, hinting at environmental differences that affect evolutionary trajectories. These variances elucidate why some galaxies flourish while others languish, presenting a tapestry of cosmic diversity that invites further exploration.
The intricacies surrounding cosmic dust also extend into the realm of exoplanetary science. Dust plays an indispensable role in the formation of planetary systems around young stars. The coagulation of dust grains into larger bodies, termed planetesimals, is critical for the eventual emergence of planets. Furthermore, the presence of cosmic dust impacts the thermal balance and chemical makeup of protoplanetary disks, dictating the conditions necessary for organic compounds to form—the precursors to life as we understand it.
Moreover, cosmic dust is an essential element in astrobiology, the study of potential extraterrestrial life. The organic molecules, including amino acids and hydrocarbons, can be synthesized on cosmic dust grains. When these grains deliver their contents to planetary bodies through impacts, they may provide the necessary ingredients for abiogenesis, the process by which life arises from nonorganic precursors. This nexus between dust and life’s origins amplifies humanity’s fascination with cosmic clumps, as it intertwines the evolutionary path of the universe with our quest for understanding existence itself.
Despite its insidious presence on a cosmic scale, the study of dust also presents complex challenges. The small size and widespread distribution of these particles render them notoriously difficult to observe. Advanced techniques such as infrared spectroscopy and scattering methods have been developed to overcome these obstacles, allowing researchers to analyze the composition and structure of cosmic dust in unprecedented detail. These technological advances not only foster deeper scientific understanding but also enrich the narrative of cosmic assembly and formation, challenging and refuting previously held notions.
In summation, the exploration of cosmic dust through the lens of the CODAG Chronicles unveils a tapestry of interconnectedness that captivates both the scientific community and the general populace. The fundamental role of dust aggregations in cosmic formation, coupled with their profound implications for life’s origins, reveals a universe that is both dynamic and inherently relatable. Cosmic clumps are not mere artifacts of stardust; they embody the life cycles of stars and, by extension, the genesis of life itself. This cyclical relationship between creation and destruction, culmination and inception, reflects a fundamental truth about existence: we are intertwined with the cosmos in ways both mysterious and magnificent. Each grain of dust encapsulates a narrative that begs to be told—a testament to the intricate dance of celestial forces shaping our universe.