As humanity grapples with the exigencies of climate change and the depletion of conventional energy resources, the quest for sustainable living has gained unprecedented urgency. The concept of living off-grid—especially through the harnessing of solar power—has emerged as an attractive alternative, particularly in countries endowed with abundant sunlight like Brazil. This exploration delves into the viability of a solar-powered off-grid lifestyle in Brazil, focusing on the myriad factors involved, including geographical considerations, system requirements, economic facets, and societal implications.
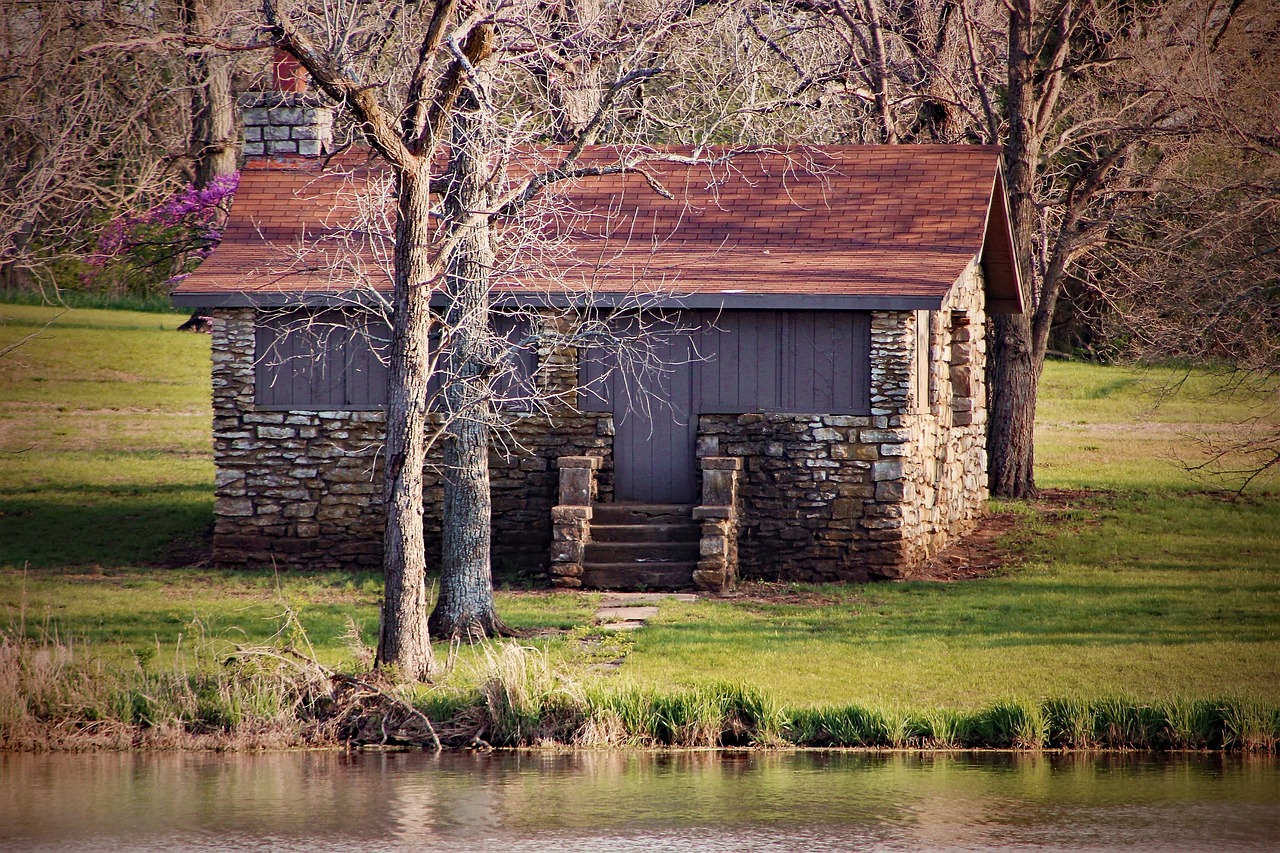
Brazilian topography presents an extraordinary pallet for solar energy utilization. With its geographical vastness, the nation benefits from both tropical and subtropical climates, offering more than 2,500 hours of sunshine annually in numerous regions. Particularly in the northeastern states, such as Bahia and Pernambuco, sunlight is strikingly abundant. This natural advantage fosters a convincing case for the implementation of photovoltaic systems—a key technology for converting sunlight into usable electrical energy.
Another critical aspect impacting the feasibility of living off-grid with solar power in Brazil is the availability of appropriate technology. Photovoltaic (PV) panels, commonly employed in solar energy systems, have seen significant advancements in efficiency and affordability. These panels can be installed on residential rooftops or even as ground-mounted systems on larger plots of land. Additionally, the integration of energy storage solutions such as lithium-ion batteries mitigates the intermittent nature of solar energy. By storing excess energy generated during the day, inhabitants can utilize this power during nights or overcast days, thereby ensuring a continuous supply of electricity.
Nevertheless, one must also consider the intricacies involved in designing a solar power system tailored to off-grid living. The first step involves evaluating energy needs. Residents must meticulously assess their consumption patterns, which depend on the number of occupants, appliances used, and lifestyle habits. Considerations often include refrigeration, cooking, lighting, and water pumping. A comprehensive energy audit facilitates the accurate calculation of the requisite solar array size and battery storage capacity, serving as a foundation for a sustainable off-grid system.
Beyond initial energy assessments, installation entails understanding the local regulatory landscape. In Brazil, solar energy initiatives benefit from progressive governmental policies and incentives aimed at promoting renewable energy adoption. Various financial mechanisms, including low-interest loans and tax exemptions, may facilitate the transition to a solar-powered lifestyle. However, navigating the bureaucratic processes can present challenges, with regional disparities often complicating the interpretation of national laws at the local level. Engaging local experts or firms that specialize in renewable energy can provide invaluable assistance in overcoming these hurdles.
Economic feasibility emerges as another pivotal concern. While the upfront investment required to procure and install a solar power system can be considerable, a thorough cost-benefit analysis is essential. Over time, financial savings manifest through reduced or even eliminated electricity bills, particularly in remote areas where grid access is limited or unavailable. Additionally, the long-term reliability of solar energy, coupled with potential increases in grid electricity prices, reinforces the attractiveness of this sustainable option. Furthermore, for those interested in agrarian ventures, solar-powered irrigation systems can translate into enhanced agricultural productivity, reinforcing economic resilience.
Addressing the social implications of living off-grid with solar power in Brazil is equally essential. Often, the decision to lead an off-grid lifestyle is not purely driven by economic necessity but also by ethical considerations. Many individuals and communities are increasingly motivated by sustainability, self-sufficiency, and environmental stewardship. As Brazil continues to face pressing environmental challenges—deforestation, loss of biodiversity, and polluted waterways—the transition to renewable energy is increasingly viewed as an ethical imperative. Moreover, solar power can empower marginalized communities by providing reliable electricity where grid access is absent, thereby enhancing quality of life and fostering local economies.
Furthermore, the rise of off-grid living through solar energy can promote a shift in cultural attitudes. The ethos of sustainability becomes ingrained within local communities, fostering collective efforts towards environmental conservation and responsible resource management. Initiatives such as community solar projects and collective energy cooperatives can reinforce social bonds, thereby replacing isolated living with a sense of communal purpose and responsibility.
However, complex challenges persist. The integration of solar power into everyday life requires not only technological adoption but also changes in consumption behaviors. Habitual reliance on high-energy-consuming devices must shift towards energy-efficient solutions. This adjustment can serve as a catalyst for broader conversations about sustainable living and environmental consciousness within Brazilian society.
In conclusion, while the prospect of living off-grid using solar power in Brazil is laden with potential, it requires a confluence of multiple factors—geographical advantages, appropriate technology, economic viability, regulatory frameworks, and societal attitude shifts. As Brazil stands on the precipice of an energy revolution, the collective endeavors of individuals, communities, and governments can lead to sustainable and transformative changes in energy consumption, fostering an environment where off-grid living becomes not only possible but preferable. The journey toward a solar-powered future is complex and multifaceted, yet profoundly rewarding for both individuals and the planet.