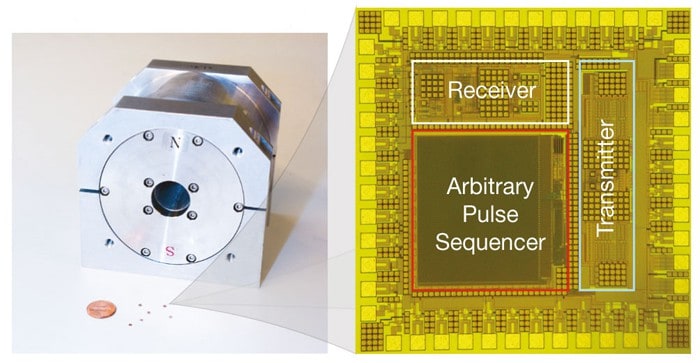
The advent of mobile technology has catalyzed significant transformations across myriad scientific domains, including the realm of spectroscopy. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, a stalwart technique within analytical chemistry and molecular biophysics, has not been exempt from this evolution. Traditionally characterized by its intricate apparatus and requirement for stable laboratory conditions, NMR spectroscopy is now witnessing a paradigm shift toward mobility. This transition is not merely a reflection of technological advancement, but also underscores a more profound fascination with accessibility and adaptability in scientific inquiry.
At its core, NMR spectroscopy exploits the magnetic properties of atomic nuclei to elucidate the structure, dynamics, and interactions of molecules. It has garnered acclaim for its ability to provide detailed insights into molecular architectures, particularly within complex biological systems. Despite its advantages, conventional NMR instrumentation is typically large, expensive, and immobile, which has historically limited its application in field studies and remote analyses. However, recent innovations have heralded the advent of portable NMR devices that maintain the efficacy of traditional systems while providing unparalleled flexibility.
The emergence of portable NMR spectrometers invites an exploration of several compelling phenomena. First and foremost, it addresses a common observation in the scientific community: the pressing need for on-site analytical capabilities. Many scientific endeavors, particularly those in environmental monitoring, food safety, and clinical diagnostics, necessitate immediate results that mobile NMR technology can facilitate. By bringing the laboratory to the field, researchers can conduct real-time analyses that yield crucial data without the lag time associated with transporting samples to a stationary laboratory. This immediacy not only enhances research outcomes but also promotes timely decision-making in critical situations.
Moreover, the allure of mobile NMR spectroscopy extends beyond mere convenience; it embodies a deeper philosophical shift regarding the democratization of science. In fields previously dominated by specialized labs, the introduction of portable NMR technologies enables a broader array of scientists, including those in academia, industry, and even citizen science initiatives, to engage with sophisticated analytical techniques. This widespread accessibility fosters a collaborative spirit among diverse research communities and encourages interdisciplinary approaches that marry physics, chemistry, and biology. In this light, the fascination with mobile NMR becomes intertwined with aspirations for inclusivity within the scientific process.
Though increased accessibility is laudable, it is imperative to acknowledge the inherent challenges that accompany the transition to mobile NMR. Chief among these challenges is the trade-off between resolution and portability. Many portable NMR devices, while lightweight and user-friendly, may not achieve the same spectral resolution as their bench-top counterparts. This disparity raises critical questions about the reliability and accuracy of data obtained in non-traditional settings. Addressing these concerns requires rigorous calibration protocols and a nuanced understanding of the limitations posed by different mobile systems. Researchers must reconcile their aspirations for mobility with the necessity for robust, reproducible results.
Despite these challenges, the integration of mobile NMR spectroscopy with complementary technologies has proven to be a fruitful avenue for overcoming some of the inherent limitations of portable devices. For instance, the combination of NMR with miniaturized mass spectrometry and other analytical modalities opens new frontiers for compound characterization and quantitative analysis. By leveraging the strengths of each technique, scientists can attain a more comprehensive understanding of complex samples, even in less-than-ideal environments. The potential for synergistic innovation through interdisciplinary collaboration enhances the charm and intrigue surrounding mobile NMR applications.
The fascination with mobile NMR spectroscopy is further fueled by its diverse applications across various research fields. In the agricultural sector, for instance, portable NMR models are being employed to assess soil health and monitor nutrient composition in crops. Such initiatives not only have far-reaching implications for food security but also reinforce sustainable agricultural practices. Likewise, portable NMR has found utility in the medical field, where it can be used for non-invasive assessments of tissues and the detection of metabolites in vivo. Such advancements carry transformative potential, paving the way for more personalized medicine and improved health outcomes.
In conclusion, going mobile with NMR spectroscopy encapsulates a significant evolution in both technology and the scientific ethos. As the lines between traditional laboratory work and field-based research continue to blur, the opportunities for exploration and discovery become increasingly enthralling. While the allure of mobile NMR lies in its convenience and accessibility, its true value resides in fostering a culture of inclusivity and collaboration across scientific disciplines. The road ahead is fraught with challenges—ensuring reliable data, enhancing resolution, and integrating innovative technologies—but the potential for transformative impact renders the endeavor profoundly worthwhile. The future of NMR spectroscopy, particularly in its mobile incarnation, promises a fascinating journey into the interplay between science, technology, and the quest for knowledge.