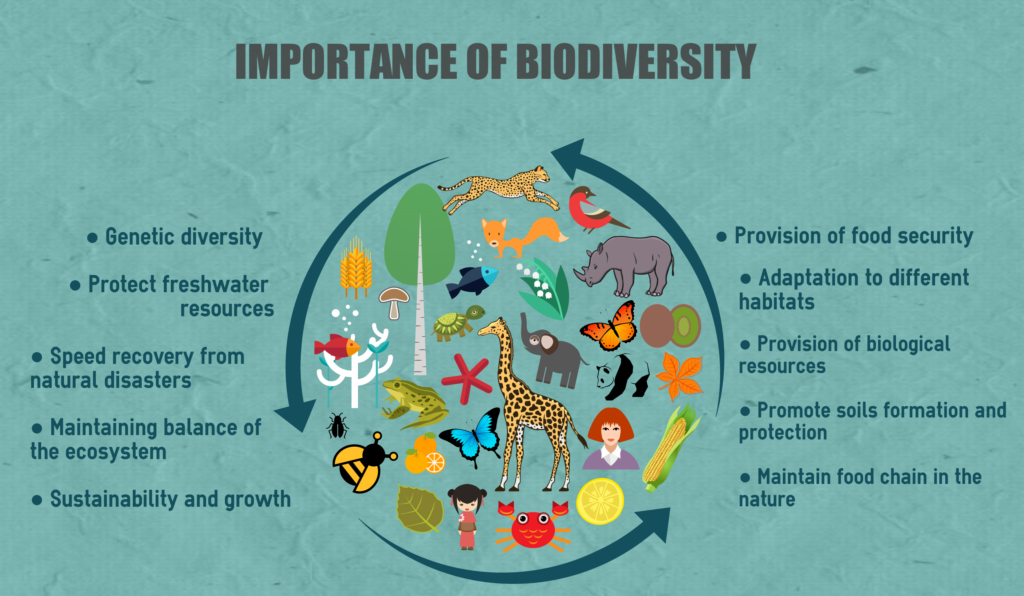
Biodiversity, the exquisite tapestry of life, serves as the foundation upon which the delicate balance of ecosystems rests. This multifaceted concept encompasses the vast array of species, their genetic variations, and the complex ecosystems in which they interact. Each thread in this intricate weave contributes to the environmental fabric, bestowing crucial services that sustain life on Earth. This article delves into the pivotal roles of biodiversity in environmental stability, ecological resilience, and the facilitation of essential processes.
The Pillars of Ecosystem Functionality
At its core, biodiversity enhances ecosystem functionality, akin to a symphony where each instrument plays a distinct yet harmonious role. From the smallest microorganism to the towering trees, each organism contributes to nutrient cycling, pollination, and food production. Various species interact in myriad ways. For instance, plants absorb carbon dioxide, release oxygen, and form the base of food webs, while herbivores ensure plant diversity through grazing, and predators regulate herbivore populations. This interdependence fosters a dynamic equilibrium, essential for sustaining life.
Ecological Resilience: Nature’s Safety Net
Biodiversity acts as nature’s safety net, providing resilience against environmental perturbations. Just as a diverse portfolio mitigates financial risks, a rich variety of species bolsters ecosystem stability against stresses such as climate change, disease, and habitat destruction. Ecosystems rich in biodiversity exhibit enhanced resilience; they can recover from disturbances with greater speed and efficiency. For instance, coral reefs teeming with diverse marine species can rebound from bleaching events far better than those with a homogeneous composition. This resilience is paramount as human activities increasingly threaten natural environments.
Carbon Sequestration and Climate Regulation
The role of biodiversity in climate regulation cannot be overstated. Forests, wetlands, and grasslands act as significant carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide and mitigating climate change. Diverse plant species enhance the efficiency of carbon sequestration. For example, mixed forests, which harbor a variety of tree species, are more effective at absorbing CO2 than monocultures. The intricate relationship between flora and fauna within these ecosystems contributes to a stable climate, illustrating the profound implications biodiversity has on global environmental health.
Pollination: The Unseen Architects of Food Security
Pollination is another vital function where biodiversity plays a critical role. Many of the crops that serve as staples in human diets depend on the intricate dance of pollinators. Bees, butterflies, birds, and bats, each contribute to the successful reproduction of flowering plants. The decline of these pollinator species poses a dire threat to global food security, emphasizing biodiversity’s crucial role in maintaining agricultural productivity. By cultivating diverse habitats, we not only safeguard these essential pollinators but also enhance crop yields and nutritional variety.
Soil Health and Fertility
The profound impact of biodiversity extends beneath the soil as well. A rich community of microorganisms, fungi, and invertebrates is integral to soil health and fertility. These organisms decompose organic matter, recycling nutrients and forming humus, which in turn sustains plant growth. Functional diversity among soil organisms ensures comprehensive nutrient availability and promotes robust plant life, thereby supporting the entire biosphere. This underground network epitomizes how biodiversity underpins not just the terrestrial environment but also agricultural systems that feed billions.
The Intersection of Ecosystem Services and Human Well-Being
The significance of biodiversity transcends ecological parameters, extending into the realm of human well-being. Ecosystem services, ranging from clean water and air to recreational opportunities, are intricately linked to biodiversity’s presence and health. The preservation of diverse ecosystems directly correlates with human health, as these environments provide resources for medicine, food, and cultural enrichment. Loss of biodiversity, thus, threatens not only the environment but also the socio-economic fabric of human societies—undermining livelihoods that depend on ecosystem services.
Cultural and Aesthetic Value
Beyond the tangible benefits, biodiversity enriches human cultures and imbues landscapes with aesthetic value. Diverse flora and fauna inspire art, literature, and traditions, fostering a sense of belonging and identity among communities. The rich biodiversity of ecosystems also serves as a reservoir of knowledge, with indigenous cultures often possessing profound insights into the ecology of their local environments. The intrinsic value of biodiversity evokes a sense of stewardship—one that emphasizes the ethical obligation to protect and preserve the myriad forms of life that share our planet.
Global Implications and Conservation Efforts
In an increasingly globalized world, the implications of biodiversity loss reverberate across ecosystems and nations. The interconnectedness of life necessitates collaborative efforts for conservation, transcending geographical boundaries. Initiatives such as protected areas, biodiversity corridors, and sustainable practices are critical in safeguarding diverse ecosystems. Global frameworks like the Convention on Biological Diversity advocate for the conservation of biological diversity, sustainable use of its components, and equitable sharing of benefits arising from genetic resources. These collective actions underscore the imperative of integrated approaches to conservation, balancing ecological integrity with human aspirations.
Conclusion: A Call to Action
In summary, the roles of biodiversity in the environment are vast and interconnected, forming an intricate web that supports life as we know it. Recognizing and valuing biodiversity is crucial for promoting ecological health, food security, and human well-being. As stewards of the Earth, humanity bears the responsibility to preserve this exquisite tapestry of life for future generations. The time to act is now, fostering a world where biodiversity flourishes, enhancing not only the environment but also our very existence. Embracing the richness of biodiversity is not merely an option; it is an imperative for sustaining life on our planet.