In the intricate and ever-evolving world of science and engineering, the concept of material technology has emerged as a cornerstone of innovation and advancement. At its core, material technology encompasses the study, design, and application of materials to develop new products and improve existing ones. But what exactly does this mean, and more intriguingly, can we envision the implications of material technology on our everyday lives? As we delve into the realm of material technology, a playful question arises: How might our interaction with the physical world evolve as materials become more advanced and adaptive? This inquiry leads us to consider not only the benefits but also the challenges posed by such technological advancements.
Material technology is fundamentally multidimensional, combining elements of physics, chemistry, and engineering. It seeks to understand the relationship between the structure of materials at the atomic or molecular level and their macroscopic properties. This investigation is critical in determining how materials can be manipulated to achieve desired characteristics such as strength, durability, and conductivity. As we venture deeper into this expansive field, we must acknowledge the various classifications that define materials: metals, ceramics, polymers, and composites, each with unique attributes and applications.
One of the most remarkable aspects of material technology is its historical significance. From the Bronze Age, marked by the advent of metals, to today’s digital age, characterized by sophisticated electronic components, each phase of development has been driven by advancements in material science. Early humans utilized available materials to craft tools and shelter, laying the groundwork for future innovations. In contemporary society, material technology plays a pivotal role in industries ranging from aerospace to biomedical engineering, reflecting its vast and varied applications.
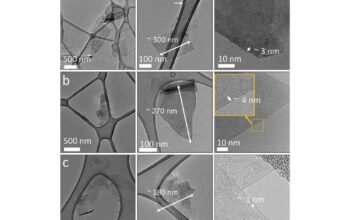
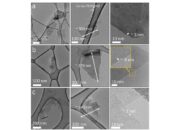
The synthesis of new materials often lies at the heart of technological advancements. Researchers are now developing nanomaterials, which exhibit extraordinary properties due to their minuscule size. These materials can enhance everything from solar cells to drug delivery systems, presenting solutions to some of the most pressing challenges of our time. Yet, as we marvel at the possibilities, we must also grapple with the ethical implications of such innovations. Will the widespread adoption of nanotechnology lead to unforeseen environmental consequences, or could it exacerbate socioeconomic disparities?
Durability and sustainability are also principal concerns within the domain of material technology. As the global community becomes increasingly aware of environmental issues, there is a heightened demand for materials that can withstand the test of time while minimizing ecological footprints. Biodegradable plastics, recyclable composites, and bio-inspired materials are paving the way towards a more sustainable future. The challenge lies not merely in creating alternative materials but in integrating them effectively into existing manufacturing processes without compromising quality or performance. Could this integration be the key to marrying innovation with sustainability?
Another avenue of exploration in material technology is the development of smart materials. These adaptive materials respond dynamically to environmental stimuli, such as temperature, light, or pressure. For example, shape memory alloys can return to a predetermined shape upon heating, presenting opportunities for self-healing structures and adaptive devices. The question arises: How might these innovations transform industries reliant on conventional materials? The potential applications are staggering, from aerospace components that can adjust to aerodynamic changes to medical implants that can change form based on the body’s requirements.
As we scrutinize the advancements in material technology, it is crucial to consider the implications of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning within this field. By harnessing AI, researchers can expedite the discovery of new materials by predicting the properties of compounds before they are synthesized in the lab. This integration of AI could lead to breakthroughs that significantly accelerate the pace of innovation. However, does this reliance on technology create a dependency that may stifle human ingenuity in the long run? How do we ensure that human intuition and creativity remain at the forefront of material design?
Moreover, the significance of material technology extends far beyond the industrial sector; it profoundly impacts societal progress. From the construction of resilient infrastructures in disaster-prone areas to the enhancement of medical devices that improve health outcomes, material technology shapes the fabric of modern civilization. Yet, as we celebrate these advancements, we must also be vigilant about equitable access to new materials and technologies. Can we ensure that the benefits of material technology are distributed fairly, or will inequities persist, leaving some communities behind?
As we navigate the complex landscape of material technology, the exploration of new frontiers reveals neoteric challenges that can reshape industries and societies. The interplay between innovation, sustainability, and ethics presents a multifaceted puzzle that researchers, engineers, and policymakers must collectively address. Can we harness the power of advanced materials to create a sustainable future while ensuring equitable access for all? The answer, though uncertain, is crucial as we embark on this transformative journey.
In summation, material technology represents a vibrant nexus of scientific inquiry and practical application. It is an arena where curiosity meets creativity, and where the past informs the future. As we delve into this fascinating field, the continuous inquiry into how materials impact our lives and the environments we inhabit will remain paramount. The evolution of material technology poses not only great potential for revolutionary change but also a reflective challenge to consider its broader implications for humanity.