In the realm of measurement instruments, integrating meters stand out due to their unique capability to accumulate and display integral quantities over time. These devices are pivotal across various domains, including electrical engineering, fluid mechanics, and environmental monitoring. They provide not merely a snapshot of instantaneous conditions but encapsulate a more profound narrative by aggregating data points into a comprehensive picture. This characteristic of integrating meters not only facilitates a nuanced understanding of various processes but also sparks intellectual curiosity regarding their principles of operation and applications.
1. Understanding Integrating Instruments
Integrating instruments are defined by their ability to measure the total quantity of a variable over a specified duration. Unlike traditional meters that provide instantaneous readings, integrating meters function to accumulate data, revealing trends and behaviors that could otherwise remain hidden. This accumulation process involves integrating physical quantities such as voltage, current, mass flow, or any other measurable variable.
Integrating meters can be classified into two primary categories: direct and indirect integrators. Direct integrators compute the integral of the input signal in real-time, while indirect integrators use stored data to compute the integration over a designated period, offering flexibility in various applications.
2. Types of Integrating Meters
To delve deeper into the world of integrating instruments, it is essential to explore the various types that exist, each tailored to specific applications:
2.1 Electronic Integrators
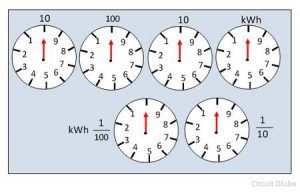
Electronic integrating meters utilize digital circuits and algorithms to perform complex computations instantaneously. These meters are widely employed in electrical applications, where they measure the total energy consumed over time. Electric energy meters often fall under this category, calculating kilowatt-hours (kWh) based on the cumulative energy usage of appliances.
2.2 Mechanical Integrators
Mechanical integrating meters, on the other hand, employ purely physical mechanisms, such as gears and dials, to visually represent the accumulated measurement. These are often found in older installations and industrial settings, where direct visual feedback is essential. Despite their declining prevalence due to digital advancements, mechanical integrators still hold significance in specific contexts, particularly in historical studies of measurement technology.
2.3 Flow Integrators
Flow integrators are specialized instruments used in hydraulics and fluid dynamics. They measure the total volume or mass of a fluid that passes through a particular point over time. Their ability to aggregate flow data is critical in industries such as water management, oil and gas, and chemical processing, where understanding total throughput can indicate system performance and efficiency.
3. The Fascination with Integration
The intrigue surrounding integrating meters encompasses more than mere functionality; it taps into broader scientific and engineering principles. The concept of integration itself resonates deeply with numerous fields of physics and mathematics. Given that these instruments compute total quantities, they embody an essential mathematical operation that transcends the mere numerical. This connection fosters an appreciation for the underlying theories and applications in real-world scenarios.
Consider the measurement of electrical energy consumed by an appliance. An integrating meter not only provides a figure but also embodies a continuous process of energy usage, allowing for empirical analysis of efficiency and sustainability. The versatility of integrating meters enables them to serve as a bridge between abstract science and tangible results, captivating researchers and engineers alike.
4. Applications of Integrating Meters
The applications of integrating meters are diverse, spanning industrial, commercial, and environmental sectors:
4.1 Industrial Energy Management
In industrial settings, integrating meters play a crucial role in energy management systems. They facilitate the optimization of energy consumption, allowing industries to monitor trends and implement measures to reduce operational costs. Such integrations contribute to sustainability initiatives, emphasizing the importance of energy efficiency and resource conservation.
4.2 Environmental Monitoring
In the environmental sector, integrating meters are vital for tracking pollutant levels, water quality, and meteorological data over prolonged periods. For instance, integrating meters that measure chemical concentrations in water bodies enable researchers and policymakers to assess environmental health and devise strategies for remediation and conservation.
4.3 Renewable Energy Systems
With the burgeoning interest in renewable energy sources, integrating meters are indispensable for assessing the total energy output from systems such as solar panels and wind turbines. By providing essential data for system performance evaluation, these instruments underpin advancements in sustainable energy technologies.
5. The Future of Integrating Instruments
As technology advances, integrating meters are poised to evolve further. Innovations in sensor technology, data analytics, and connectivity promise to enhance their efficacy and precision. The seamless integration of integrating meters with the Internet of Things (IoT) stands to revolutionize how data is collected and interpreted, enabling real-time monitoring and instantaneous feedback across numerous applications.
Conclusion
Integrating meters represent a powerful amalgamation of technology and science. Their ability to convert transient measurements into aggregated insights illuminates their significance in multiple domains. By facilitating a holistic view of processes, ranging from energy consumption to environmental impact, these instruments invite a continuous exploration of the relationship between data accumulation and informed decision-making. As society increasingly leans toward data-driven solutions, the relevance and utility of integrating meters will only expand, showcasing the essential role they play in our understanding of the world.