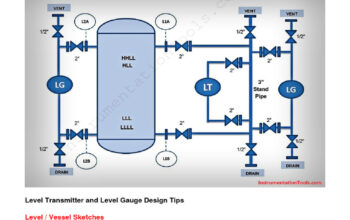
Embarking on the intricate journey of learning electronics from the ground up can be as exhilarating as it is daunting. The vast array of components, principles, and applications can be overwhelming, yet each of these elements represents a building block that contributes to the mesmerizing world of electronic systems. The key to mastering electronics lies not only in understanding its language but also in nurturing a mindset that embraces exploration and experimentation.
To initiate this intellectual expedition, one must first cultivate a foundational understanding of basic electrical concepts. It is imperative to comprehend the fundamental principles of voltage, current, and resistance, often encapsulated in Ohm’s law. Voltage is the force that pushes electrical charges through a circuit, current is the flow of these charges, and resistance restricts that flow. Grasping these concepts will provide you with a framework to delve deeper into the realm of electronics.
Following this foundational step, familiarization with common electronic components is essential. Resistors, capacitors, diodes, transistors, and integrated circuits serve as the backbone of most electronic devices. Each component has unique characteristics and functions, yet they often work in concert to achieve complex behaviors. For instance, diodes allow current to flow in only one direction, making them crucial in rectification processes. Similarly, transistors serve as switches or amplifiers, enabling the modulation of electrical signals. Gaining hands-on experience with these components will solidify your understanding through practical application.
In tandem with component recognition, one must learn how to read and interpret circuit diagrams. Schematics are the blueprints of electronic devices, illustrating how components are interconnected. Developing the skill to discern symbols and connections is akin to learning a new language; it opens up expansive avenues for communication within the field of electronics. Numerous online resources and textbooks offer guides on schematic symbols, aiding in the acclimatization to this vital skill.
The journey of learning electronics also necessitates the acquisition of technical tools. A fundamental toolkit typically includes a multimeter for measuring voltage, current, and resistance, as well as a soldering iron for assembling components onto a circuit board. Breadboards are invaluable for prototyping circuits without permanent connections, allowing for flexibility and experimentation. Embrace the notion that errors are opportunities for growth; the iterative process of trial and error is often where the most profound learning occurs.
Simultaneously, immersing oneself in the rich literature of electronics can provide insightful perspectives and methodologies. Classic texts in the field, such as “The Art of Electronics” by Horowitz and Hill, can serve as comprehensive references, while online platforms, including forums and educational sites, foster community-driven learning. Engaging with this literature not only reinforces theoretical knowledge but also imbues one with the historical context and evolution of electronic principles.
The advent of digital platforms has revolutionized modern learning methods. Online courses and tutorials provide structured pathways through complex topics, often with interactive components that facilitate practical application. Websites dedicated to e-learning offer courses that range from beginner to advanced levels, encompassing an array of subjects. Such resources can be instrumental in demystifying challenging concepts through guided instruction.
Project-based learning is another pivotal strategy when beginning to navigate the world of electronics. Undertaking small projects can bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application. Start with simple circuits, such as blinking LED lights or basic sound generators, and gradually progress to more complex systems, such as microcontroller-based projects. This experiential approach not only solidifies learning but also ignites creativity and innovation, as the satisfaction from building a functioning device reinforces your newfound skills.
Networking with fellow electronics enthusiasts presents another enriching facet of the learning journey. Join maker spaces, engineering clubs, or online communities where like-minded individuals congregate to share ideas, troubleshoot problems, and collaborate on projects. Engaging with a community can provide fresh insights and diverse perspectives, accelerating your understanding of various concepts. Mentorship opportunities can also arise within these circles, offering guidance from those more advanced in their knowledge.
As your competence in electronics expands, diversifying your interests within the field can yield even greater rewards. Explore areas such as robotics, embedded systems, or renewable energy solutions. Each subfield offers a plethora of applications and can connect to broader societal challenges, thus presenting the opportunity to contribute meaningfully to technological advancements. The multidisciplinary nature of electronics invites curiosity and fosters innovation across numerous domains.
Ultimately, reflecting on the learning process is crucial to developing a deeper understanding and a more substantial retention of information. Consider maintaining a learning journal to document your experiences, challenges, and insights. This practice not only facilitates a better retention of knowledge but also allows you to track your progress over time, serving as a source of motivation during challenging times.
In conclusion, embarking on the electrifying voyage of learning electronics from scratch requires a blend of curiosity, perseverance, and a strategic approach. By grounding yourself in foundational concepts, engaging with components and circuit diagrams, and immersing yourself in practical application, you set the stage for profound discoveries. Embrace the allure of experimentation, foster collaborative relationships, and explore diverse realms within the discipline. The world of electronics awaits, brimming with potential and opportunities for innovation—an invitation to shape the future through understanding and creativity.