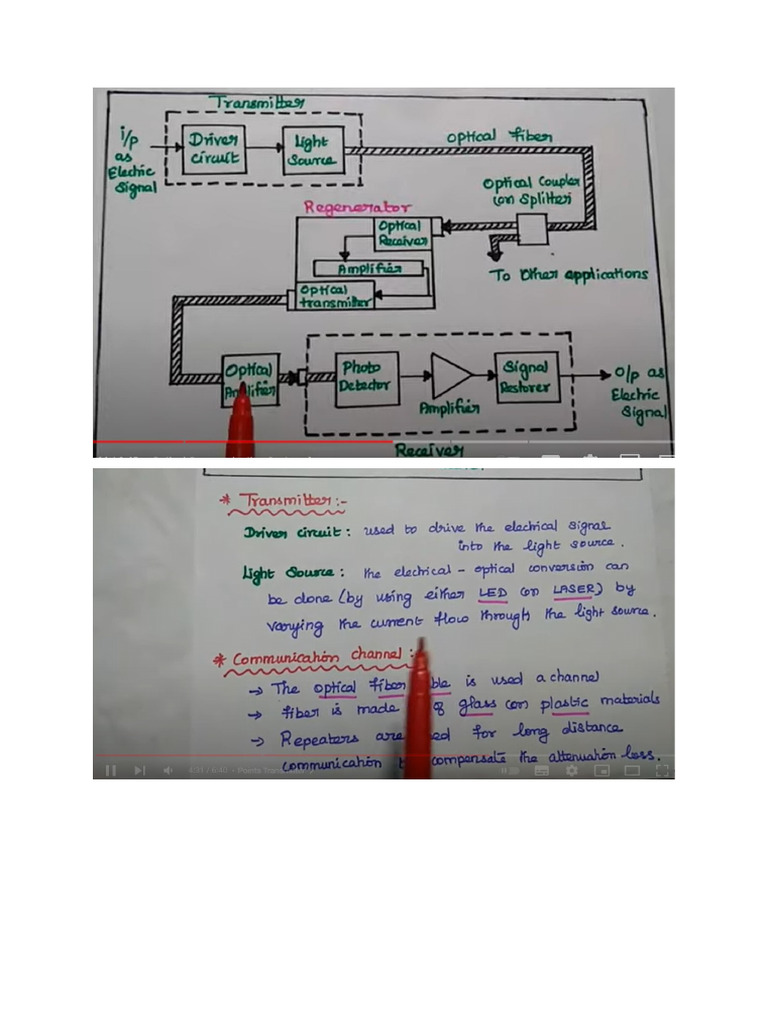
Fiber optics have revolutionized the domain of audio transmission, offering a plethora of advantages over traditional copper wire systems. This transition from electrical to optical signals redefines the paradigms of performance, quality, and flexibility. Herein, we delve into the myriad benefits presented by fiber optics specifically for audio applications, illustrating the enhanced capabilities they facilitate.
1. Superior Sound Quality
The foremost advantage of employing fiber optic technology for audio is the unparalleled sound quality it delivers. Fiber optics transmit data as light pulses, significantly reducing signal degradation that plagues conventional electrical cables. This characteristic allows for the retention of pristine audio details across expansive distances, rendering sound reproduction remarkably faithful. With increased bandwidth, fiber optics can handle greater quantities of audio data, making them ideal for high-definition audio formats.
2. Immunity to Electromagnetic Interference
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) poses a persistent challenge in audio engineering, particularly in environments laden with electronic devices. Fiber optic cables, by virtue of their construction, are impervious to EMI. Unlike their copper counterparts, which can pick up interference and introduce noise into the signal chain, fiber optics provide a clean and unadulterated audio transmission path. This quality is instrumental in maintaining audio integrity in professional studio settings and during live performances, where clarity is paramount.
3. Enhanced Transmission Distance
Another compelling advantage of fiber optics is their capacity for long-distance audio transmission without signal loss. Copper wires succumb to attenuation over distances greater than a hundred meters, necessitating repeaters or boosters to sustain audio quality. In contrast, fiber optic systems can transmit signals over several kilometers without any significant degradation, making them suitable for complex setups in concert halls, stadiums, and large venues. This feature not only reduces the need for extensive equipment but also minimizes the potential for audio lag.
4. Lightweight and Space-Efficient Design
Fiber optic cables are considerably lighter and more compact than traditional copper cables, which possess bulky dimensions and substantial weight. This inherent advantage enables easier installation in various settings, from intimate recording studios to expansive concert arenas. The reduced weight not only simplifies the logistics of handling and laying cables but also alleviates the stresses on mounting hardware and infrastructure, promoting a streamlined setup that is both aesthetically pleasing and functional.
5. Increased Security
In the contemporary age of audio transmission, security cannot be overlooked. Fiber optic cables offer enhanced security features due to their inability to emit signals outside the cable itself. This characteristic significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized data interception, a concern pertinent in both professional and private audio exchanges. Consequently, fiber optics serve as a secure alternative for streaming sensitive audio data, particularly for confidential communications and high-profile events.
6. Future-Proof Technology
The rapid evolution of audio technologies necessitates a robust and adaptable transmission medium. Fiber optics stand as a future-proof solution, capable of accommodating advancements in audio standards and formats. As emerging technologies like 3D audio and high-resolution audio continue to gain traction, fiber optics can readily support the bandwidth requirements that accompany such innovations, ensuring longevity and relevance in an ever-changing technological landscape.
7. Versatility
The versatility of fiber optic systems in audio applications cannot be overstated. Fiber optics can interconnect a myriad of devices, from microphones and mixing boards to speakers and amplifiers, creating a cohesive audio network. This adaptability allows for integration with various audio protocols, enhancing functionality and enabling creative configurations tailored to specific audio environments. Additionally, fiber optic solutions can interface with digital and analog systems alike, facilitating a smooth amalgamation of legacy technologies with modern components.
8. Cost Efficiency Over Time
Although the initial investment in fiber optic infrastructure can be higher than traditional systems, the long-term advantages often outweigh the initial costs. Fiber optics exhibit durability and longevity, reducing the frequency of replacements and associated maintenance expenses. Furthermore, their resilience to environmental factors curtails the risk of operational disruptions, thus providing a more reliable system overall. The efficiency in installation and reduced need for extensive equipment translates to lower operational costs over time.
9. Environmentally Friendly
As society increasingly prioritizes sustainability, the environmental impact of technology becomes an essential consideration. Fiber optic cables generally consume less power during transmission compared to their copper counterparts. The manufacturing process for fiber optics also involves fewer harmful chemicals, thereby minimizing ecological harm. By adopting fiber optic technology, audio engineers can significantly reduce their carbon footprint, aligning their practices with global sustainability goals.
10. Innovation in Audio Experiences
Finally, the adoption of fiber optics fosters innovation in the audio experience itself. High-capacity data transmission can facilitate unique audio applications such as immersive sound environments, virtual reality audio, and advanced surround sound systems that draw heavily on the capabilities of fiber optics. As creators harness the potential of these technologies, the boundary between audio reception and experience continues to blur, promising to engage listeners in unprecedented ways.
In conclusion, the advantages of utilizing fiber optics for audio are both diverse and profound, spanning aspects of sound quality, transmission integrity, security, and adaptability. As technology continues to evolve, the integration of fiber optics presents a compelling pathway toward an enriched auditory landscape—poised to redefine how sound is transmitted, perceived, and experienced in the modern era.