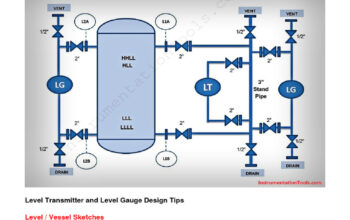
Nuclear engineering is a multifaceted discipline that encompasses the design, construction, and operation of nuclear reactors, as well as the safe handling of radioactive materials. For a budding scholar at 14 years old, the ambition to delve into nuclear engineering can seem daunting yet tantalizingly approachable. This article seeks to illuminate pathways, resources, and methodologies to cultivate a burgeoning interest in this complex field.
Understanding Nuclear Engineering
At its core, nuclear engineering is the study of the processes and principles of nuclear reactions. It is a discipline steeped in the juxtaposition of rigorous scientific inquiry and cutting-edge technological innovation. Young enthusiasts often find themselves captivated by the transformative potential of nuclear energy, which promises vast quantities of energy with minimal greenhouse gas emissions. However, this fascination may also stem from a deep-seated curiosity regarding the fundamental nature of matter and energy.
The Importance of a Strong Foundation in Math and Science
Before immersing oneself in the intricacies of nuclear engineering, it is imperative to establish a solid foundational understanding of mathematics and the sciences. Courses in algebra, calculus, physics, and chemistry are essential. Mathematics serves as the language of engineering, enabling the formulation of complex models and calculations. Physics, particularly, provides insight into the behavior of particles and energy, which is crucial for understanding nuclear processes.
Expanding Knowledge through Reading
Engaging with textbooks and literature dedicated to nuclear engineering can foster a deeper understanding of the subject. Notable texts include ‘Introduction to Nuclear Engineering’ by John R. Lamarsh, which elucidates fundamental concepts through a structured approach. Additionally, reviewing materials from reputable online platforms and academic journals can offer insights into current research trends and breakthroughs within the field.
Utilizing Online Resources and Courses
The digital era has democratized access to education. Numerous online platforms offer courses in nuclear engineering and related fields. Websites such as Coursera, edX, and Khan Academy provide interactive learning experiences that are both engaging and informative. Enrolling in introductory courses focused on physics and engineering not only enhances knowledge but also familiarizes one with advanced concepts in an approachable manner.
Participating in Science Competitions
Participation in science fairs and engineering competitions is an excellent way to practically apply knowledge while sparking creativity. Events such as the Science Olympiad or the FIRST Robotics Competition allow participants to engage collaboratively in problem-solving and engineering design. These competitions often feature categories that relate to nuclear science, providing a platform to showcase one’s understanding and innovate solutions.
Finding Mentorship
Forming connections with professionals in the field can be instrumental for aspiring nuclear engineers. Networking with teachers, attending seminars, and leveraging platforms like LinkedIn to connect with industry experts can yield mentorship opportunities. A mentor can provide invaluable insights into academic choices, career paths, and emerging technologies, aiding significantly in navigating one’s educational journey.
Engaging with Local Educational Institutions
Many universities and community colleges offer summer programs or workshops for high school students interested in STEM fields. Investigating local technical institutions for courses focusing on nuclear or radiological engineering can further enrich understanding. These programs often combine theoretical knowledge with hands-on experiences, providing practical skills and exposure to the field.
Exploring Internships and Volunteer Opportunities
Seek internships or volunteer experiences with organizations involved in the energy sector, particularly those focusing on nuclear energy. Junior volunteer opportunities at local science museums or research facilities allow for exposure to real-world applications of nuclear engineering principles. Such experiences not only build impressive resumes but also serve to solidify interest in the field.
Participating in Public Engagement and Awareness Initiatives
Public discourse surrounding nuclear energy is often fraught with misconceptions. Actively engaging in debates or forums, or conducting informational campaigns about the benefits and challenges of nuclear energy can sharpen communication skills and deepen knowledge. Understanding societal perspectives on nuclear engineering fosters a well-rounded approach to the field’s ethical and practical implications.
Continuing Education Beyond High School
The journey towards a career in nuclear engineering necessitates rigorous academic commitment beyond high school. Pursuing a bachelor’s degree in nuclear engineering or a related discipline is fundamental. Not only does it prepare individuals with specialized knowledge, but it also equips them with problem-solving skills that are essential in the workforce. Graduate studies may be beneficial for those interested in research or high-level positions in the industry.
Conclusion: The Road Ahead
Embarking on a journey into nuclear engineering at the age of 14 can lead to a myriad of rewarding experiences and opportunities. With determination, curiosity, and a strategic approach to education, young aspiring engineers can begin to lay the groundwork for a successful career. Through the confluence of rigorous study, practical application, networking, and engagement with local and global communities, the intricate world of nuclear engineering can transform from a distant goal into an attainable reality.