Quantum computing represents an unprecedented shift in the landscape of technology and its implications for society. As we stand on the verge of this quantum frontier, one may ponder: how will quantum computing profoundly influence the everyday lives of the common man? This tantalizing inquiry opens the door to numerous possibilities, while concurrently presenting a formidable challenge in understanding and accessing this emerging technology. In this exploration, we will dissect the myriad ways quantum computing could reshape individual experiences, enhance societal operations, and ultimately democratize the benefits of advanced computing.
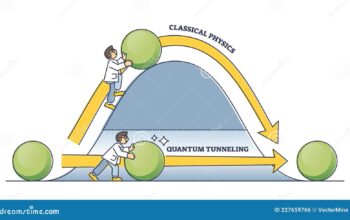
The fundamental advantage of quantum computing lies in its ability to process information in ways that classical computers cannot. Classical computers utilize bits as the smallest unit of data, represented as either 0 or 1. Conversely, quantum computers leverage quantum bits, or qubits, which can exist in superpositions of states, enabling them to perform complex calculations at incomprehensible speeds. This unique capability raises the following question: how will these spectacular computational feats translate into tangible benefits for the average person?
First, consider the realm of healthcare. The quantum revolution promises to catalyze significant advancements in personalized medicine and drug discovery. Traditional methods of drug development are notoriously time-consuming and financially burdensome. Quantum computing can accelerate the simulation of molecular interactions, identifying potential drug candidates with astounding efficiency and accuracy. Imagine a world where a tailored medication is available at your local pharmacy, designed specifically for your genetic profile. Such enhanced precision in treatments could significantly improve health outcomes and minimize the side effects often associated with one-size-fits-all pharmaceuticals.
Furthermore, quantum computing could dramatically enhance diagnostic capabilities. Advanced machine learning models—powered by quantum algorithms—could rapidly analyze medical data, such as genomic sequences, medical imaging, and electronic health records, leading to earlier diagnosis of diseases. The development of non-invasive diagnostic techniques could transform how we approach health, making screenings for conditions like cancer easier, cheaper, and more accessible.
In addition to healthcare, the world of finance stands to benefit immensely from quantum technologies. Financial institutions are constantly searching for ways to enhance their predictive models, manage risks more effectively, and optimize portfolios. The processing power of quantum computers could revolutionize these efforts. For the everyday individual, this means potentially more stable financial services, lower fees, and access to personalized financial products. The specter of quantum computing could result in a more equitable financial landscape, where everyone, regardless of socioeconomic status, could tap into advanced financial analytics previously reserved for large corporations.
Moreover, consider how quantum computing can impact the field of cybersecurity. With the advent of quantum technologies, the nature of encryption will inevitably evolve. Classical encryption methods might become obsolete in the face of quantum algorithms that can break standard cryptographic codes with relative ease. While this poses a significant challenge, it also stimulates the development of quantum-resistant protocols, ensuring that personal data remains secure in an increasingly digital world. The average person would thus benefit from a safer online experience, with enhanced privacy and protection against cyber threats.
Addressing climate change is another daunting challenge that quantum computing may help tackle. By modeling complex systems in real-time and addressing variables that classical computers cannot, quantum algorithms could optimize energy usage and streamline resource management. The analysis of vast datasets related to climate patterns can lead to better predictive models and tailored strategies for reducing emissions. For individuals, this translates into more sustainable living practices and energy-efficient technologies that could lower household costs while promoting environmental stewardship.
In the realm of logistics and transportation, quantum computing could revolutionize supply chain management. For instance, consider the simplicity of ordering a product online. Behind the scenes, efficient routing of delivery vehicles and real-time inventory management are imperative to ensure timely delivery. Quantum computers can optimize these processes with unparalleled speed, minimizing delays and reducing operational costs. The outcome? Enhanced convenience and potentially lower prices for everyday consumers.
Yet, amidst this optimistic outlook, it must be emphasized that the transition to quantum computing presents significant hurdles. Public understanding of such a complex field is imperative for widespread acceptance and integration. There exists a palpable challenge in bridging the knowledge gap and demystifying quantum advancements for the common man. Educational initiatives that inspire curiosity and promote accessibility to quantum technologies will be crucial in embedding these innovations deeply into societal frameworks.
Moreover, the financial investment required to harness the full potential of quantum computing may exacerbate existing inequalities. As resources are funneled into advanced research and development, a rigorous ethical framework is necessary to ensure that the benefits of this technology are equitably distributed. This brings forth the question of governance: as quantum computing catalyzes transformation across numerous sectors, how will policymakers address the ethical implications and potential disparities that may arise?
In retrospect, while quantum computing harbors the potential for radical enhancement of the common man’s life—from healthcare and finance to environmental sustainability and cybersecurity—the realization of such benefits hinges upon effective education, policy, and inclusive practices. The future may be quantum, but navigating this realm requires collective effort and a commitment to making these advancements accessible to all. As we continue to ponder the implications of quantum computing, it is equally essential to address the challenges it presents, ensuring that this powerful tool serves humanity as a whole.