Graphene, often dubbed the “wonder material” of the 21st century, has emerged as a beacon of innovation in various fields, transcending traditional boundaries and offering revolutionary applications. In dentistry, this remarkable allotrope of carbon is not merely an adjunct but rather a transformative agent that could redefine preventive and restorative treatments. This article delves into the multifaceted applications of graphene in the domain of dentistry, uncovering its potential to enhance patient outcomes and improve material performance.
1. Overview of Graphene’s Properties
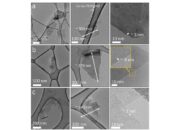
Graphene is a two-dimensional lattice of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal configuration, renowned for its unparalleled strength, electrical conductivity, and biocompatibility. With a tensile strength approximately 200 times greater than that of steel, it possesses the ability to withstand substantial forces, rendering it an ideal candidate for dental materials. Moreover, its exceptional electrical properties pave the way for innovative diagnostic and therapeutic tools in oral health.
The uniqueness of graphene lies not only in its robustness but also in its thinness—a mere one atom thick. This singularity allows it to interlace seamlessly with other materials without compromising the integrity of dental structures. Consequently, graphene’s incorporation into dental applications signifies an intersection between the macroscopic and the microscopic, much like a fine needle threading through a tapestry.
2. Enhancing Dental Materials
The integration of graphene into composite resins and dental cements heralds a new era of materials science. These enhancements ensue from the incomparable mechanical properties of graphene, which can augment the strength and durability of traditional composites. By achieving an optimal dispersion of graphene in polymer matrices, researchers have demonstrated significant improvements in compressive strength, flexural strength, and wear resistance of the resulting composites.
This fortified resilience is akin to a fortress with a graphene-infused foundation, capable of resisting not only the daily wear of mastication but also the chemical assaults posed by dietary acids. Such advancements in dental materials directly correlate with diminished rates of restoration failure, offering patients lasting solutions in an era where transient fixes can often lead to frustration.
3. Antimicrobial Properties
Oral health is intrinsically linked to the presence of multifarious microorganisms, with pathogenic strains often leading to dental caries and periodontal diseases. Enter graphene, with its remarkable antimicrobial properties. Studies have illuminated its ability to disrupt bacterial membranes, effectively neutralizing harmful pathogens, thereby serving as a potent agent in preventive dentistry.
Imagine graphene as a vigilant guardian of the oral cavity, forming an invisible barrier that not only resists invasions from nefarious bacteria but also promotes a healthier biome. The incorporation of graphene into dental coatings and sealants can significantly augment resistance to biofilm formation, making it an indispensable ally in the fight against oral diseases.
4. Innovative Diagnostic Tools
In a realm where early detection is paramount for successful treatment, graphene’s electrical properties are being harnessed to design advanced diagnostic tools. Graphene-based sensors can detect low-concentration biomarkers present in saliva, facilitating the monitoring of oral diseases and systemic conditions. These non-invasive tools offer rapid results, transforming the paradigm of dental diagnostics from reactive to proactive.
This development is akin to equipping a watchful sentinel with a magnifying glass, capable of identifying potential threats long before they manifest into full-blown maladies. By integrating these sensors into routine dental visits, practitioners can better assess patient health, promote preventive strategies, and ultimately enhance treatment outcomes.
5. Regenerative Approaches
Graphene’s biocompatibility opens avenues for tissue engineering within dentistry, particularly in the regeneration of periodontal tissues and bone. Utilizing graphene scaffolds can significantly improve cell attachment, proliferation, and differentiation, vital processes for tissue regeneration. The synergistic combination of graphene with stem cells presents revolutionary possibilities in periodontal therapy—akin to a gardener nurturing seeds into flourishing plants.
Current advancements in regenerative dentistry could enable patients to regenerate lost structures efficiently, reducing the reliance on more invasive surgical interventions. Graphene-laden scaffolds are envisaged to play a central role in this transition, providing a conducive environment for tissue growth and facilitating the body’s innate healing processes.
6. Future Prospects and Challenges
The integration of graphene into dentistry is not without challenges. Researchers face hurdles such as cost-effective production and scalability, ensuring that the promise of graphene can translate into widespread clinical applicability. Moreover, regulatory considerations remain a significant barrier, as the assessment of graphene’s long-term biocompatibility and toxicity must be rigorously conducted before clinical adoption.
Yet, as the landscape of dental technology evolves, the potential of graphene to enhance both aesthetic and functional aspects of dental care cannot be overstated. The trajectory of research indicates an impending revolution, much like the dawn of composite resin materials that transformed restorative dentistry decades ago.
Conclusion
Graphene emerges as a multifaceted entity in dentistry, serving as a crucial ally in enhancing materials, preventing diseases, innovating diagnostics, and pioneering regenerative practices. As we stand on the brink of a graphene-fueled future, the convergence of technology and material science promises to reshape dental practices. This remarkable material is not just a testament to scientific ingenuity but a harbinger of a healthier and more resilient future for oral health.