In the realm of renewable energy, China’s ambitious foray into solar thermal technology represents a strategic and multifaceted investment in clean energy solutions. The nation embraces this innovative approach with a vigor that reflects both its environmental aspirations and economic imperatives. China’s unabated quest for sustainable energy has garnered global attention, as its investment in solar thermal power positions it as a bespoke leader in the clean energy sector.
Solar thermal energy, a method that harnesses the sun’s heat to generate electricity, offers a promising alternative to conventional fossil fuel-based energy systems. Unlike photovoltaic systems that convert sunlight directly into electricity, solar thermal technologies utilize mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight, thereby producing high-temperature heat, which can subsequently be converted into power through thermodynamic cycles. This approach not only addresses the pressing issue of greenhouse gas emissions but also capitalizes on an abundant and renewable resource—the sun itself.
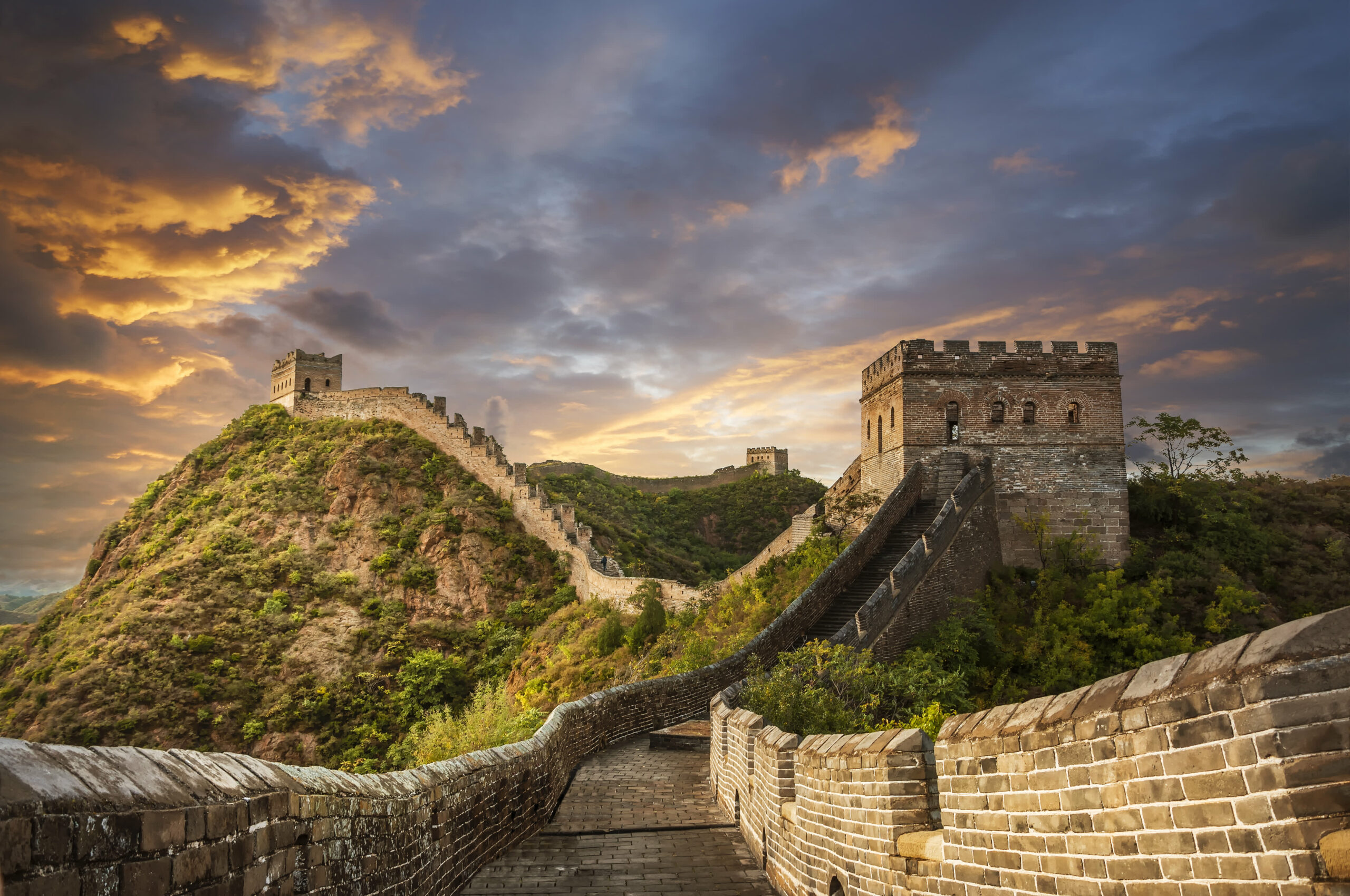
The sheer scale of China’s solar thermal investments is staggering. In recent years, the nation has enacted policies facilitating the proliferation of solar thermal installations, leading to a significant increase in both the number and sophistication of concentrated solar power (CSP) plants. A telling hallmark of China’s commitment to this technology is the construction of large-scale CSP projects, which have been pivotal in establishing a robust infrastructure capable of supporting and advancing solar thermal capacities.
At the district heating level, solar thermal systems provide vast benefits, particularly in urban landscapes where demand for heating is a constant. The integration of solar thermal systems into residential buildings not only enhances energy efficiency but can also reduce reliance on coal-fired heating systems, a prevalent source of urban pollution in many Chinese cities. By replacing traditional coal consumption with solar alternatives, China strives to mitigate air quality issues while enhancing energy security.
Notably, the integration of solar thermal technologies dovetails with China’s overarching objective of energy diversification. Reliance on a singular energy source is precarious; thus, augmenting the energy mix with solar thermal solutions ensures greater resilience against market fluctuations and geopolitical uncertainties. This diversification mitigates energy dependency, paving the way for a sustainable future.
The economic ramifications of adopting solar thermal energy are also profound. As global energy markets evolve, demand for cleaner alternatives is surging. By positioning itself at the forefront of solar thermal energy production, China cultivates an environment conducive to innovation, localization, and job creation. The solar thermal industry is poised to stimulate significant employment opportunities across manufacturing, installation, and maintenance sectors, amplifying the economic discourse surrounding energy transition.
In concert with economic advantages, China’s engagement in solar thermal technology signifies its broader commitment to international climate agreements, such as the Paris Accord. By enhancing its domestic capability and technology, China not only showcases its ambitions to curtail carbon emissions but also reaffirms its status as a significant player in global environmental governance. The embrace of solar thermal energy enables Chinese policymakers to publicly commit to ambitious targets, including substantial reductions in fossil fuel use by mid-century.
Furthermore, the societal acceptance of solar thermal energy forms a critical component of its successful implementation. Public awareness campaigns and educational initiatives are crucial in informing citizens about the benefits of solar thermal systems. These efforts correlate positively with increased public adoption and can engender a culture of sustainability, further catalyzing momentum for renewable energy technologies throughout China.
However, the path toward a solar thermal-dominated energy landscape is fraught with challenges. Technological advancements must continually evolve to improve efficiency and reduce capital costs associated with solar thermal installations. Moreover, competition from existing traditional energy sources remains a formidable hurdle. As such, stakeholders within the energy sector must engage in cooperative ventures that promote research and development initiatives aimed at overcoming these obstacles.
Another pivotal aspect is the need for carefully constructed policy frameworks that support the sustainable growth of solar thermal energy. Regulatory support and fiscal incentives could stimulate investment from both domestic and international players. Emphasizing the importance of R&D funding and favorable regulations would likely bolster the expansion of solar thermal capacity while ensuring environmental sustainability.
International collaboration presents yet another avenue for enhancing China’s solar thermal expertise. Cooperative efforts with countries experienced in solar thermal technologies could lead to knowledge exchange, driving innovation and expediting the development of advanced systems tailored to local conditions. Such partnerships could serve as catalysts for rapid technological advancements, propelling China into a leading position not just in production but also in innovation.
In conclusion, China’s strategic embrace of solar thermal energy encapsulates a broader ambition to pivot towards sustainable energy systems. The intersection of technological innovation, economic opportunity, and environmental stewardship underscores the rationale behind this commitment. As China embarks on this transformative journey, it holds the promise of reshaping its energy landscape while fortifying its standing in the global race toward a green future. Through unwavering dedication and concerted policy efforts, China is poised to lead by example in harnessing the sun’s potential, crafting a sustainable narrative that might inspire nations worldwide.