Being a quantum mechanics physicist is an intellectually stimulating journey that traverses the realms of fundamental science, mathematical abstraction, and practical application. As one delves into this captivating domain, numerous facets of the discipline come to light—each offering a unique perspective and an assortment of challenges. This article elucidates the multifaceted nature of a career in quantum mechanics, examining the diverse types of content that characterize the experiences of professionals in this field.
The first aspect to consider is the profound theoretical foundation that undergirds quantum mechanics. This discipline operates at the juncture of classical physics and modern physics, presenting a collection of paradigms that can defy common intuition. Concepts such as wave-particle duality, uncertainty principle, and quantum entanglement serve as pivotal elements that quantum physicists must grasp. Engaging with the intricate mathematics of Hilbert spaces, operators, and wave functions is a routine yet exhilarating endeavor. Natural philosophies are reinterpreted, pushing the boundaries of what one perceives to be an absolute reality.
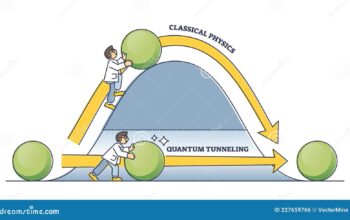
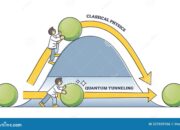
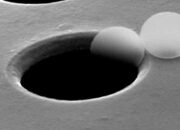
Moreover, a quantum mechanics physicist frequently encounters paradoxes that challenge conventional thought processes. For instance, the famous double-slit experiment unfurls not only a fascinating demonstration of wave-particle duality but also provokes philosophical inquiries into the nature of observation. Each day brings new revelations, forcing physicists to reconceptualize their understanding of the universe. This blend of challenging ideas and philosophical reflection fosters an environment ripe for intellectual growth, drawing physicists deeper into the esoteric layers of quantum behavior.
Beyond theoretical inquiry, research is an integral component of a physicist’s career. Quantum mechanics offers multiple avenues for exploration, including quantum computing, quantum cryptography, and condensed matter physics. In pursuing experimental research, physicists often collaborate in interdisciplinary teams, combining expertise from fields such as engineering, computer science, and materials science. Through meticulous experimentation, they probe quantum phenomena, seeking to validate theories or discover new properties of quantum systems. This empirical approach necessitates a robust understanding of both the theoretical underpinnings and the technological tools at their disposal.
The transition from theory to experimental practice is a critical part of a quantum physicist’s career. It entails design of experiments that must consider quantum decoherence, measurement challenges, and the inherent limitations imposed by uncertainty principles. Ensuring accuracy and precision can be daunting, as even minuscule disturbances can alter outcomes in substantial ways. Such challenges require a physicist to become adept at critical thinking and problem-solving, often crafting innovative methodologies to obtain reliable data.
A pivotal aspect of being a quantum physicist is the dissemination of knowledge. Effective communication, whether through research papers, conference presentations, or public lectures, is essential for fostering collaboration and inspiring future generations. The ability to elucidate complex topics to a diverse audience ranges from fellow physicists to educators and laypersons. Clarity in communication is paramount; thus, physicists cultivate a lexicon that navigates the fine line between technical accuracy and accessible explanation.
Moreover, the ever-evolving landscape of quantum research compels physicists to remain abreast of rapid advancements in the field. The advent of quantum technologies holds enormous promise for diverse applications, from advanced medical imaging techniques to revolutionary computing paradigms. Continuous professional development is integral to the role, necessitating attendance at conferences, workshops, and seminars to discuss emergent theories and applications. Keeping pace with this dynamic field often spurs collaborative projects and ongoing dialogue among peers, creating a vibrant academic community.
Interdisciplinary collaboration is another hallmark of a quantum physicist’s career. Often, the intersection of disciplines can result in groundbreaking innovations. For instance, quantum biology is an intriguing field that examines the role of quantum effects in biological processes, inviting physicists to engage with biologists and chemists. This collaborative spirit fosters an enriching environment that breeds creativity and innovation. As problems become increasingly complex, solutions from a broad spectrum of expertise are required to propel understanding forward.
The workplace environment for quantum mechanics physicists can vary widely; they may be found in academic institutions, government research laboratories, or private industry settings. Each setting presents its own unique dynamics and emphasizes different priorities. In academia, the focus often gravitates toward research and teaching, where mentoring the next generation of scientists becomes a significant responsibility. Conversely, in private industry, the emphasis may skew towards practical applications, necessitating a keen understanding of market trends and consumer needs.
Another dimension of a physicist’s life is the challenge of funding and resource allocation. Securing grants and sponsorship is a perennial concern, with researchers often required to justify their inquiries in a competitive landscape. This process can be taxing and requires adept skills in proposal writing and project design. Understanding the bigger picture of societal needs helps physicists align their research with funding opportunities, thereby fostering a sustainable career trajectory.
Ultimately, the journey of a quantum mechanics physicist is profoundly rewarding, albeit challenging. The intertwining of rigorous theoretical constructs, innovative experimental designs, collaborative endeavors, and effective communication yields a profession that influences the very fabric of technology and understanding the universe. The exploration of quantum mechanics is not merely an academic pursuit; it is an enterprise that continuously reshapes humanity’s comprehension of existence itself.
As physicists venture forth, they are not only tasked with solving the enigmas of quantum behavior but also with imparting knowledge, inspiring curiosity, and fostering innovation. In embracing this path, one embarks on a lifelong journey marked by discovery, collaboration, and the relentless pursuit of understanding.