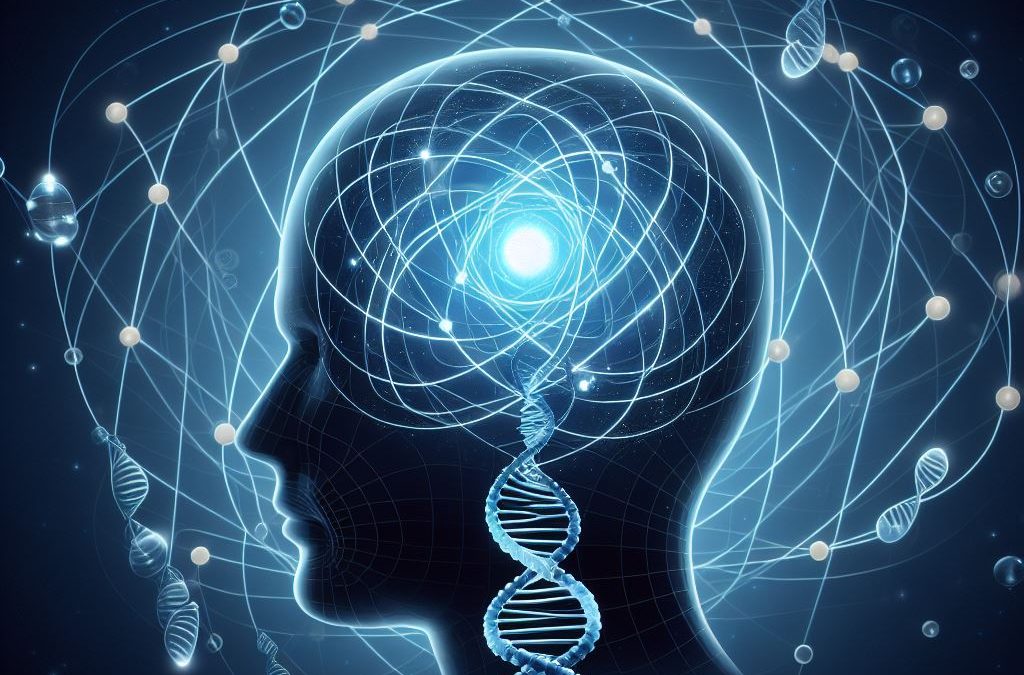
Consciousness remains one of the most perplexing phenomena in the realm of science, particularly in the disciplines of physics and cognitive science. The transition from mere atoms—considered the fundamental building blocks of matter—to the complex conceived understanding within the realm of consciousness raises profound inquiries. How did consciousness arise from non-conscious entities? This inquiry has led to the exploration of various interconnected domains, from the biological underpinnings of thought to the foundational principles of physics that govern the universe.
To commence with the physical perspective, we must apprehend what atoms truly are. Atoms, the smallest units of matter, comprise protons, neutrons, and electrons. Their interactions are dictated by the laws of physics, predominantly quantum mechanics. The intricate dance of particles within and around atoms lays the groundwork for the molecular compositions that eventually culminate in biological life. However, our quest is not merely to understand matter; it is to delve into how this matter morphs into conscious experience.
To elucidate this transformation, we must consider the emergence theory, which posits that consciousness is an emergent property arising from specific complex systems. Within this framework, it becomes essential to explore what constitutes a complex system. In biological entities, atoms combine to form molecules, which, through various biochemical pathways, lead to the development of cells. These biological units further aggregate to form tissues and organs, significantly encoding information in the form of neural networks within the brain.
The brain, composed of approximately 86 billion neurons, serves as a remarkable organ for processing information. Each neuron functions through electrochemical signals, contributing to a vast network of communication. It is within these neural circuits that the essence of thought, perception, and ultimately, consciousness germinates. These interconnected networks exhibit properties that may not be discernible at the atomic level—thus illustrating the principle of emergence, wherein collective behavior supersedes the sum of individual actions.
Moreover, the concept of integrated information theory (IIT) offers an intriguing perspective. IIT posits that consciousness correlates with the degree of information integration within a system. Simply put, for a system to be conscious, it must not merely receive and process information but must also integrate it into a unified whole. This leads to the consideration of how synaptic connections in the brain represent an intricate web of information processing, potentially granting rise to subjective experience.
From the biological lens, the advent of consciousness might be linked to evolutionary advantages. Conscious entities exhibit heightened awareness and responsiveness to their environments, thereby enhancing survival and adaptability. Theories suggest that consciousness may have evolved as a tool to facilitate the complex social interactions necessary for cooperative living. By understanding the motives and feelings of others, conscious beings can navigate social hierarchies and foster alliances that are advantageous for communal survival.
Interestingly, the exploration of consciousness transcends mere biology; it intertwines with the realms of philosophy and physics. The debate regarding whether consciousness is a fundamental aspect of the universe or a byproduct of complex biological computations echoes across disciplines. The notion of panpsychism posits that consciousness is a fundamental quality inherent in all matter. Under this paradigm, atoms themselves might possess rudimentary forms of consciousness, leading to more advanced consciousness as atoms combine into larger, more complex systems.
Furthermore, the role of quantum mechanics in consciousness adds yet another layer of complexity to this discussion. Some theorists propose that quantum processes, operating at the subatomic level, may contribute to consciousness. This hypothesis stems from the peculiar behaviors observed in quantum systems, which exhibit non-locality and superposition, analogous to some properties of conscious thought. Although widely debated, the intersection of consciousness and quantum mechanics prompts a reevaluation of the foundational understanding of reality.
In addition, the evolving field of neurophilosophy seeks to bridge the gap between neuroscience and philosophical inquiries into consciousness. This interdisciplinary dialogue serves to elucidate the nature of conscious experience and its implications for notions of free will, selfhood, and personal identity. Neurophilosophy posits that an understanding of the brain’s workings can inform philosophical discussions, thus engaging with questions once thought to reside solely within the domain of metaphysics.
Moreover, the implications of artificial intelligence (AI) have surfaced new discussions regarding consciousness. As AI systems become increasingly sophisticated, the question arises: can machines possess consciousness? While current algorithms can mimic aspects of human cognition, they languish in the realms of mere simulation devoid of authentic subjective experience. This exploration compels us to continually reassess the essence of consciousness itself and whether it can truly arise from non-biological substrates.
In summary, the inquiry into how consciousness emerged from atoms encompasses a multidisciplinary spectrum of science and philosophy. From the atomic configurations that give rise to biological complexity to the intricate workings of the human brain, the journey remains fraught with enigmatic questions and intellectual challenges. Consciousness, as an emergent phenomenon, appears to underscore the interconnectedness of physical laws, biological evolution, and the profound depths of human thought and experience. As research develops, the ongoing discourse promises continued revelations beckoning our understanding of the cosmos and our place within it.